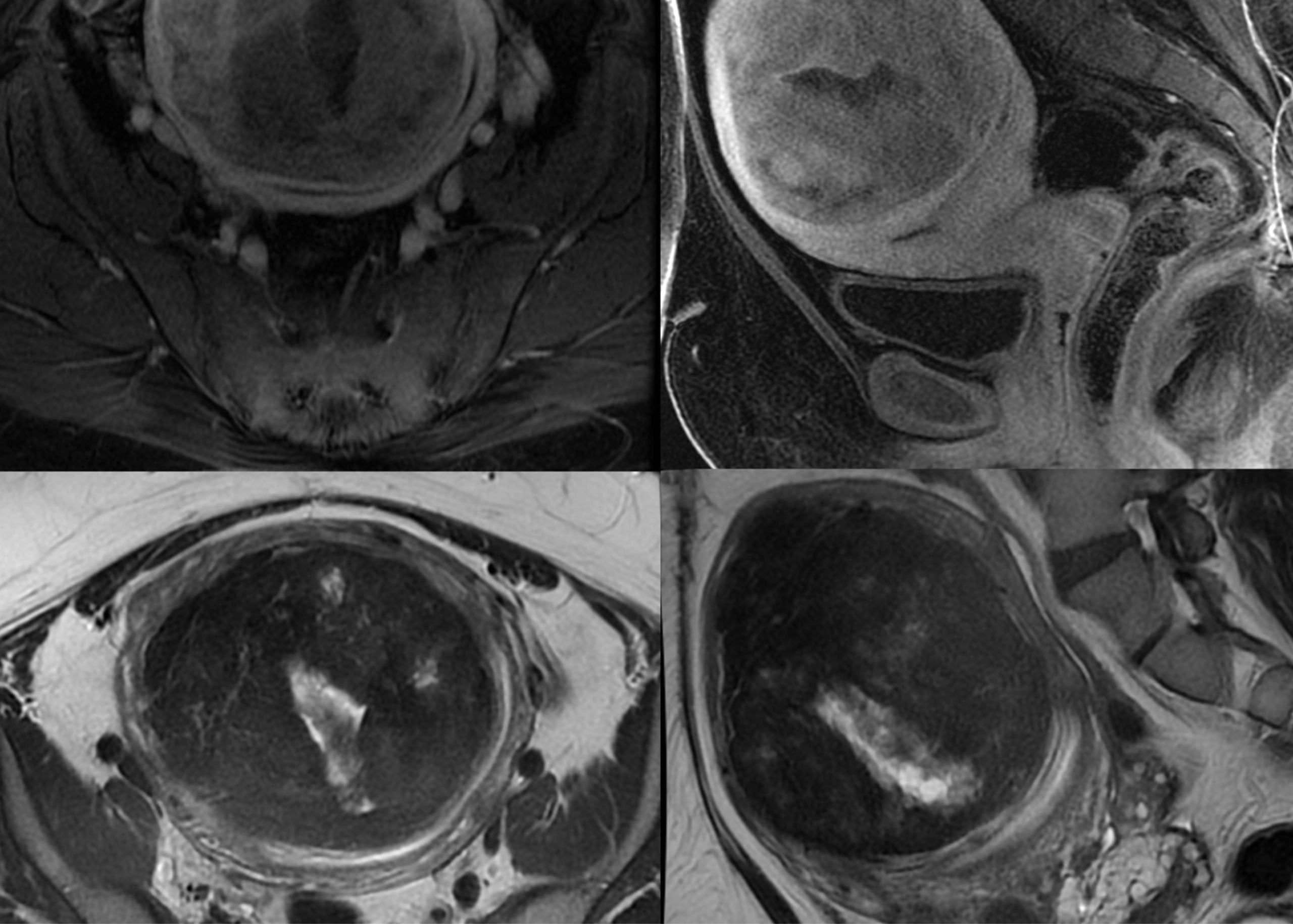
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that grow from the uterine wall. They are common in women of reproductive age and tend to grow slowly, but they can cause problems with fertility and pain.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are the most common cause of abnormal vaginal bleeding in women post-menopause; however, they can also cause pain and heavy periods in younger women. Some women may not have any symptoms associated with uterine fibroids at all. The signs may include:
- Pain during sex or deep penetration during sex (dyspareunia)
- Heavy periods (menorrhagia)
- Bleeding between periods (metrorrhagia)
- Intermenstrual spotting or bleeding (intermenstrual vaginal bleeding or intermenstrual bleeding)
Causes for Uterine Fibroids
The exact cause of is unknown. There is some evidence that they may be due to an imbalance between estrogen and progesterone hormones.
Diagnosis of Uterine Fibroids
Diagnosis is based on a medical history and physical examination. A pelvic ultrasound can be used to confirm the presence of uterine fibroids. In some cases, additional imaging tests such as MRI angiography may be used to measure the size of the fibroid and determine whether it is causing any pressure to adjacent structures like the bladder.
Importance of Treating Uterine Fibroids
If you have uterine fibroids, it’s essential to treat them because they can cause other health problems if left untreated. For example:
- Uterine fibroids can interfere with your ability to become pregnant. The larger your fibroid grows, the more likely it will block the fallopian tubes and prevent conception from occurring.
- Uterine fibroids can cause heavy menstrual bleeding, leading to anemia if left untreated or uncontrolled. Iron deficiency anemia is characterized by fatigue and weakness.
- Suppose you have uterine fibroids that are large enough to press against your bladder or rectum (which happens in about 40% of cases). They can cause constipation or urinary frequency—both symptoms of bladder diverticula or rectal prolapse, respectively.
Treatment for Uterine Fibroids
Treatment for uterine fibroids is based on the size and number of your fibroids and the severity. Your doctor will discuss your options with you to determine what’s best for you. Below are some of the treatment options
Hysterectomy: A hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus. It is performed by a gynecologist and can be done either through an abdominal incision or via laparoscopy (using small incisions). The procedure requires hospitalization. Patients need a recovery period of three months to return to normal activities.
Myomectomy: Myomectomy is the surgical removal of uterine fibroids. It is also known as uterine myomectomy or fibroid removal surgery. Myomectomies are typically done by a gynecologist or general surgeon and may require hospitalization or outpatient surgery.
High intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU): HIFU treatment occurs while you Lay in a particular MRI machine. The machine produces sound waves. These methods cause a burn inside the fibroid, which later turns into a scare. It will treat only a few fibroids, which subsequently can grow again.
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is a minimally invasive procedure that can treat fibroids without surgery. In UFE, a catheter is inserted into the uterine arteries. This catheter will help in delivering embolization material to the fibroids tumors. A substance called a “Particles” is then injected through the catheter into the fibroid tissue, which cuts off its blood supply and causes it to shrink over time; the time needed is between 3 months to 12 months. Patients start feeling better over time.
Because UFE does not require surgery, no incision is needed during your treatment. The procedure is done under local anesthesia and sedative drugs. After your system, you may experience some cramping, but this should subside within 24 hours. Most patients can return home after their treatment with instructions for self-care and follow-up care instructions from their doctor.
Advantages of Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE):
UFE has several benefits over other treatments:
- It’s minimally invasive—you won’t need general anesthesia during this procedure, and you’ll be able to go home soon with pain medication.
- It has no downtime—you’ll be able to go back to work after the procedure with no restrictions on activity.
- It’s effective—the success rate of UFE is approximately 90%, meaning that most women who have it don’t require additional treatments afterward.
- Pregnancy after an embolization — Many centers that perform Uterine artery embolization have confirmed that women who have undergone embolization can have children.
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is a less invasive alternative to hysterectomy that can help treat the symptoms of symptomatic uterine fibroids. It can be an effective treatment option for women experiencing symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and infertility due to fibroids.
Our Expert Interventional Radiologist

Dr. Mohamed Almarzooqi
Consultant Interventional Neuroradiology & Interventional Radiology
Burjeel Hospital, Abu Dhabi