-
Anesthesiology
-
Cardiology and Cardiovascular Surgery
-
Dentistry
-
Dermatology and Cosmetology
-
Diabetes and Endocrinology
-
ENT, Head and Neck Surgery
-
Family Medicine
-
General and Laparoscopic Surgery
-
Gynecology and Obstetrics
-
Internal Medicine
-
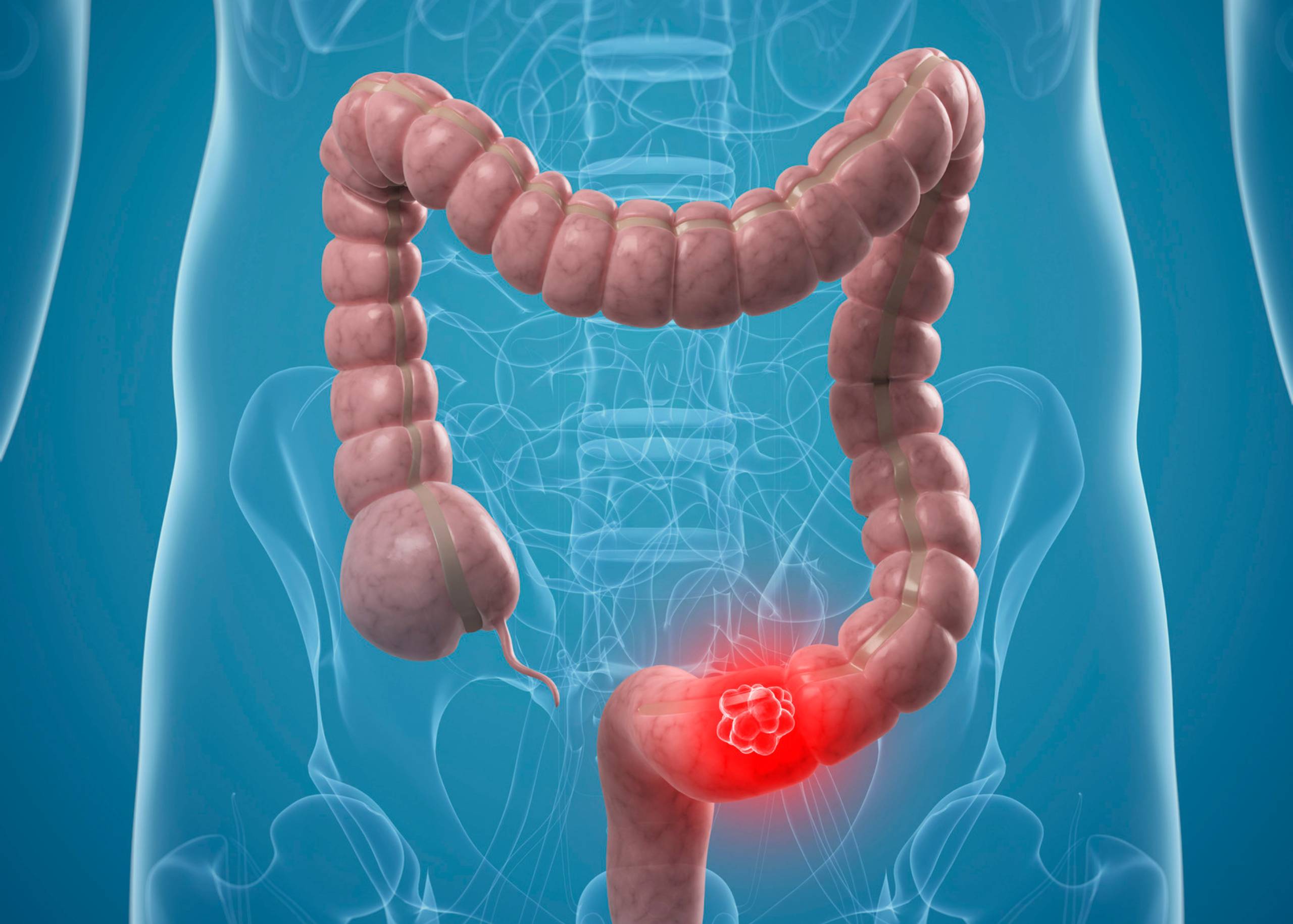
Jazzar Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease Center
-
Laser Vision Correction Center
-
Men’s Wellness and Aesthetics Clinic
-
Nader Orthopedics & Sports Medicine Center
-
Nephrology
-
Neurology
-
Neurosurgery
-
Nutrition and Dietetics
-
Ophthalmology
-
Pain Management
-
Pediatrics
-
Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
-
Plastic, Aesthetic and Reconstructive Surgery
-
Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
-
Psychology
-
Pulmonology
-
Radiology
-
Rheumatology
-
Speech Therapy
-
Spine Care Center
-
Thyroid Parathyroid Center
-
Urology
-
Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
-
Weight Management Clinic
Welcome to the newly named Jazzar Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease Center at the prestigious Burjeel Day Surgery Center, Al Reem, Abu Dhabi.
Our center is led by the renowned Dr. Ahmed Jazzar, an American Board Certified Consultant in Gastroenterology. With over 23 years of global expertise encompassing the breadth and depth of gastroenterology and interventional endoscopy, he brings a wealth of knowledge in diagnosing and treating diseases pertaining to the entire gastrointestinal tract, pancreas and liver.
Dr. Jazzar’s proficiency extends to advanced endoscopic procedures including, but not limited to, Upper Endoscopy, Colonoscopy, Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), and Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS). His extensive career heralds him as a celebrated educator, esteemed consultant, and published author in this specialty. Recognized by the American Board of Internal Medicine, he is a Fellow of both the American College of Gastroenterology and American College of Physicians, as well as a respected Member of the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy and United Network for Organ Sharing.
Services & Expertise
At the Jazzar Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease Center, our mission is to provide exceptional, world-class care through our range of services. These include the diagnosis and management of conditions such as:
- A1AD-related cirrhosis and liver disease
- Abdominal angina
- Achalasia and other esophageal motility disorders
- Acid-Peptic Disease
- Alagille syndrome and other cholestatic liver diseases
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency – liver disease in children and lung disease in adults
- Amebic liver abscess
- Ampullary cancer
- Amyloidosis involving the gastrointestinal tract
- Anal fissures, fistulas, and abscesses
- Ascites and other complications from cirrhosis
- Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Autoimmune hepatitis–Primary biliary cirrhosis overlap syndrome
- Autoimmune pancreatitis
- Balantidiasis
- Barrett’s Esophagus
- Bile duct cancer (Cholangiocarcinoma)
- Bile duct tumors
- Biliary dyskinesia
- Budd-Chiari Syndrome
- Carcinoid Syndrome
- Celiac Disease
- Cholangitis and Other Infections of the Biliary System
- Choledochal cysts
- Cholestasis
- Chronic intestinal failure
- Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction
- Chronic pancreatitis induced by autoimmune disorders, alcohol misuse, or unknown causes
- Cirrhosis and Other Liver Diseases
- Collagenous Colitis and Lymphocytic Colitis
- Colonic polyps and prevention of colorectal cancer
- Common variable immunodeficiency
- Complications and aftercare following gastrointestinal surgery
- Complications of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes
- Complications related to ostomies and pouches
- Congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency
- Constipation and disorders of defecation
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) colitis
- Diarrhea
- Diverticular Disease
- Drug-induced liver injury
- Dumping syndrome
- Enterocutaneous fistulas
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis and other allergic gastrointestinal disorders
- Eosinophilic gastroenteritis
- Erdheim–Chester disease
- Esophageal Varices
- Esophageal web or Plummer–Vinson syndrome
- Fecal incontinence and other disorders of anorectal function
- Feeding and Swallowing Difficulties
- Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular Carcinoma and other rare types of liver cancer
- Foveolar cell metaplasia
- Functional abdominal pain
- Functional gastrointestinal disorder, including dyspepsia
- Functional Gut Disorders including Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Gallbladder and Biliary Tract Disease
- Gallbladder cancer
- Gallbladder polyps
- Gallstone Ileus
- Gardner’s syndrome
- Gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE Syndrome or watermelon stomach)
- Gastric volvulus
- Gastroduodenal ulcers and Strictures
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Gastrointestinal Cancers including Stomach, Liver, Pancreatic, and Colon Cancers
- Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes
- Gastrointestinal complications of eating disorders
- Gastrointestinal complications of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
- Gastrointestinal complications of systemic diseases such as lupus, scleroderma, and rheumatoid arthritis
- Gastrointestinal disorders in pregnancy
- Gastrointestinal disorders related to opioid use
- Gastrointestinal issues related to Cystic Fibrosis
- Gastrointestinal lymphomas
- Gastrointestinal manifestations of Immunodeficiency disorders
- Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine neoplasms and Carcinoid Syndrome
- Gastroparesis
- Gaucher’s disease (and other lipid storage diseases)
- Gilbert’s Syndrome (mild hyperbilirubinemia)
- Graft-vs-host disease in the gastrointestinal tract
- H pylori infection and its complications
- Hematemesis (Vomiting Blood)
- Hematochezia (Blood in Stool)
- Hemochromatosis (Iron overload)
- Hemorrhoids
- Hepatic Artery Thrombosis
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Hepatic Vein Thrombosis
- Hepatitis and Other Infectious Liver Diseases
- Hepatitis D and Hepatitis E
- Hepatopulmonary syndrome and Portopulmonary hypertension
- Hepatorenal Syndrome
- Hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes
- Hirschsprung’s disease
- Hyper IgM Syndrome – a condition that can affect the liver and gastrointestinal system
- Hyperoxaluria and oxalosis
- Infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including parasitic infections, bacterial infections, and viral hepatitis
- Inflammatory Bowel Diseases such as Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
- Intestinal parasites
- Intestinal pseudo-obstruction
- Intrahepatic Cholestasis
- Ischemic hepatopathy
- Lactose Intolerance and other carbohydrate metabolism disorders
- Linitis plastica
- Liver abscesses and cysts
- Liver transplantation and post-transplantation care
- Malabsorption Syndromes
- Mallory-Weiss syndrome
- Maple syrup urine disease
- Meckel’s Diverticulum
- Melena
- Ménétrier’s disease
- Mesenteric Ischemia
- Metabolic and bariatric disorders
- Microscopic colitis
- Motility disorders like colonic inertia
- Niemann-Pick disease, Type C
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
- Non-alcoholic Fatty Pancreatic Disease
- Non-celiac gluten sensitivity
- Nutritional issues including vitamin and mineral deficiencies like B12 and iron deficiency anemia
- Obesity and its gastrointestinal complications
- Ogilvie syndrome (Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction)
- Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency
- Ostomy-related problems (dermatitis, retraction, prolapse, etc.)
- Pancreatic cysts
- Pancreatic Disorders including Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis
- Pancreatic fistula
- Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
- Pancreatic Pseudocysts
- Parasitic Diseases like Liver Fluke Infection, Strongyloidiasis
- Parasitic infections like amoebiasis, giardiasis, and cryptosporidiosis
- Parastomal hernia
- Pediatric Gastroenterological diseases (in cooperation with pediatric specialists)
- Peliosis hepatis (randomly distributed blood-filled cavities throughout the liver)
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
- Pneumatosis Intestinalis
- Porphyria, a group of rare genetic disorders that can affect the nervous system and the skin
- Portosystemic shunts
- Postcholecystectomy Syndrome
- Post-colitis cystitis
- Post-ERCP pancreatitis
- Post-gastric bypass hypoglycemia
- Postoperative gastrointestinal complications
- Postradiation enteropathy
- Post-surgical complications affecting the gastrointestinal tract
- Prevention and surveillance of gastrointestinal cancers
- Primary and Secondary Biliary Cirrhosis
- Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
- Primary Hyperoxaluria (causing recurring kidney and bladder stones)
- Protein-losing enteropathy
- Pseudomembranous colitis and other infectious colitis
- Pyloric stenosis
- Radiation Enterocolitis
- Rectal prolapse
- Refractory or complicated gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Rumination Syndrome
- Scleroderma – which can cause many different symptoms, including gastrointestinal ones
- Short Bowel Syndrome
- Shwachman–Diamond Syndrome (exocrine pancreatic insufficiency)
- Small bowel bacterial overgrowth syndrome
- Smoking and alcohol-related gastrointestinal diseases
- Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
- Swallowing disorders like oropharyngeal dysphagia
- Tropical enteropathy
- Tropical sprue
- Tyrosinemia (Type I, Type II)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Urea cycle disorders
- Vascular disorders of the intestine, such as ischemic colitis
- Whipple’s disease
- Wilson’s Disease, Hemochromatosis, and other hereditary liver diseases
- Yellow fever (a viral disease affecting the liver)
- Yellow Jaundice
- Zenker’s Diverticulum
- Zieve’s syndrome
- Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome and other neuroendocrine tumors
Advanced Technology Services
Our center prides itself on the use of cutting-edge technology and modern care practices. At the Jazzar Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease Center, our vision is to provide unparalleled clinical expertise that meets international standards. We foster an environment where the health and comfort of our patients are prioritized above all.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): This procedure combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat certain problems of the biliary or pancreatic ductal systems, such as gallstones, strictures or leaks.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): It combines endoscopy and ultrasound to obtain images and information about the digestive tract and the surrounding tissue and organs, including the lungs.
- 3D Imaging for Endoscopy: Advanced 3D systems provide depth perception that can enhance certain endoscopic procedures.
- Advanced Endoscopic Imaging (i-Scan, FICE): A technology that combines digital signal processing and optical filtering to enhance the quality of images during an endoscopy.
- Anorectal Manometry: This diagnostic test provides information about anorectal function for patients with constipation or fecal incontinity.
- Balloon-occluded Retrograde Transvenous Obliteration (BRTO): A procedure often used to manage gastric varices.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: A therapeutic option for eradicating Barrett’s esophagus and preventing progression to esophageal cancer.
- BilioPancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS): A complex weight-loss surgery that reduces the stomach’s size and bypasses a significant portion of the intestines.
- BRAVO PH system for GERD: A capsule-based ambulatory pH test that measures pH in the esophagus and assists in evaluating the frequency and duration of acid reflux to better understand a patient’s symptoms.
- Cholangioscopy & Pancreatoscopy: Direct visualization of the bile ducts and pancreatic ducts with small-caliber endoscopes for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions.
- Chromoendoscopy: A technique where dyes are instilled onto the gastrointestinal mucosa to enhance visualization.
- Colonic Manometry: A diagnostic procedure to understand the bowel function in patients with severe constipation and other colon-related conditions.
- Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (CLE): A technique that generates cross-sectional images of the gastrointestinal tract at the cellular level.
- Cryotherapy: Utilizes extreme cold for the ablation of dysplastic tissue in the GI tract, such as in Barrett’s esophagus or early-stage esophageal cancer.
- Digital Cholangioscopy: Provides direct visualization of bile ducts for diagnosis and management of bile duct stones and strictures.
- Endoluminal and Laparoscopic Full-thickness Plication for GERD: This is a minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgery for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Endoluminal Full-thickness Resection (EFTR): A newer technique for removing larger lesions and early-stage tumors from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR): A procedure to remove precancerous and cancerous lesions in the digestive tract.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with SpyGlass: A minimally invasive technique allowing direct visualization and treatment of pancreatobiliary system.
- Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG): A newer type of endoscopic weight loss procedure.
- Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD): An advanced technique used to remove gastrointestinal, esophageal, stomach, and early-stage colon cancers.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Biopsies (EUS-FNA and EUS-FNB): Minimally invasive technique used to obtain samples of lesions or structures within or adjacent to the gastrointestinal tract.
- Endoscopic Vacuum Therapy (EVT): Primarily employed for complicated upper gastrointestinal leaks and perforations.
- Fiducial Marker Placement: Prior to radiation therapy, endoscopic ultrasound-guided placement of fiducial markers may be performed to help accurately target tumors.
- Full Spectrum Endoscopy (FUSE): An endoscopic technology that provides a 330-degree view, which improves the ability to visualize the GI tract and potentially increases the detection rate of lesions during colonoscopy.
- Functional Luminal Imaging Probe (FLIP): This technology measures the geometric and pressure patterns in hollow organs of the GI tract, which can be useful for evaluating the function of the esophagus and the sphincter.
- G-POEM (Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy): A newer, minimally invasive procedure to help treat gastroparesis symptoms.
- Hemorrhoidal Banding: A non-surgical treatment option for hemorrhoids.
- Hepatic Elastography (FibroScan): Non-invasive method to assess liver stiffness, which closely corresponds to the degree of liver fibrosis.
- Hepatoportoenterostomy (Kasai Procedure): A surgical treatment method for biliary atresia.
- High-definition Endoscopes and Narrow Band Imaging (NBI): High-definition scopes coupled with NBI can enhance visualization of mucosal patterns and vasculature, improving the detection of dysplasia and cancer.
- Hydrogen Breath Testing: A diagnostic method to evaluate carbohydrate malabsorption and bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine.
- Intragastric Balloon Placement: A non-surgical weight loss treatment option for obesity.
- Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding (LAGB): A weight-loss procedure that involves placing a band around the upper part of the stomach to create a small pouch to hold food.
- Lumen-Apposing Metal Stents (LAMS): Used for drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts and certain types of walled-off necrosis.
- Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation (MSA): A surgical treatment for GERD where a ring of tiny magnetic beads is wrapped around the junction of the stomach and esophagus.
- Motility Testing: These are tests that measure how well the digestive tract works, used for diseases like gastroesophageal reflux disease, GERD, constipation and incontinence.
- Narrow Band Imaging (NBI): It’s an imaging modality offering enhancement for endoscopic screening, providing the possibility to detect lesions not visible under traditional white light.
- Natural Orifice Transluminal Endoscopic Surgery (NOTES): Experimental surgical methodology with the goal to reduce the invasiveness of surgical procedures.
- Endoscopic Suturing System: Allows for advanced endoscopic suturing, including closing of large defects and full-thickness tissue appositions.
- Pancreatic Pseudocyst Drainage: Drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts can be done endoscopically using a variety of techniques such as transmural or transpapillary approaches.
- Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG): A surgical procedure to place a tube for feeding those who are unable to swallow food.
- Percutaneous Endoscopic Jejunostomy (PEJ): Procedure to place a feeding tube into the jejunum (part of the small intestine) for patients who cannot take food by mouth.
- Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography (PTC): A procedure used to visualize and check the patency of the bile ducts.
- Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) Breath Test: A non-invasive method to evaluate the metabolism and effectiveness of PPI medications in GERD patients.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) for Barrett’s Esophagus: This is used to rid the esophagus of pre-cancerous cells.
- Robot-assisted Endoscopy: Emerging technology that aims to increase precision and control during endoscopic procedures.
- Single Balloon Enteroscopy (SBE): This technique is used for endoscopic visualization and treatment of diseases involving the entire small bowel.
- Thermal Ablation for Barrett’s Esophagus: A procedure that uses heat to remove precancerous tissue in the esophagus.
- Transoral Outlet Reduction (TORe): TORe is a procedure used to tighten the opening (outlet) of a gastric bypass pouch for patients who have regained weight after surgery.
Book Appointment with our Experts
Blogs

GERD and Obesity: The Connection and How to Break the Cycle
Read more
Drink Up for Digestive Health: Hydration Advice from Expert Gastroenterologists
Read more
Demystifying Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Understanding, Coping, and Thriving
Read more