Introduction
Oral cavity cancer represents a significant health challenge worldwide, with over 350,000 new cases diagnosed annually. Management of advanced cases—particularly those involving the mandible (lower jaw) and adjacent soft tissues—presents formidable surgical challenges that require sophisticated techniques to both eradicate the cancer and restore form and function. Achieving these dual goals demands a delicate balance between oncological radicality and functional-aesthetic reconstruction.
This case study examines the successful surgical management of a locally advanced oral cavity cancer at Burjeel Specialty Hospital in Sharjah, highlighting the complex decision-making process and advanced surgical techniques that enabled both effective cancer treatment and optimal functional reconstruction. The case demonstrates the importance of multidisciplinary collaboration and the application of state-of-the-art microvascular surgical techniques in achieving favorable outcomes for patients with advanced head and neck malignancies.
Understanding Oral Cavity Cancer
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Oral cavity cancer constitutes a significant proportion of head and neck malignancies globally, with particularly high incidence rates in regions where tobacco chewing, smoking, and alcohol consumption are prevalent. Key risk factors include:
- Tobacco use (smoking and smokeless forms)
- Alcohol consumption
- Chronic irritation from ill-fitting dentures or sharp teeth
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Poor oral hygiene
- Genetic predisposition
In the UAE and surrounding regions, the practice of tobacco chewing—often mixed with betel nut, lime, and other substances—remains a significant risk factor for oral cancer, particularly among expatriate populations from South and Southeast Asia.
Pathology and Progression
The vast majority (over 90%) of oral cavity cancers are squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) that arise from the mucosal lining. These malignancies typically progress through several stages:
- Early mucosal changes: Often appearing as leukoplakia (white patches) or erythroplakia (red patches)
- Carcinoma in situ: Malignant cells confined to the epithelium
- Invasive carcinoma: Penetration beyond the basement membrane
- Local advancement: Invasion into adjacent structures (muscle, bone, skin)
- Regional spread: Metastasis to regional lymph nodes
- Distant metastasis: Spread to distant organs (less common in oral SCC)
When oral SCCs involve the lower alveolus (tooth-bearing portion of the mandible), they frequently invade the underlying bone, necessitating segmental mandibulectomy as part of the surgical treatment.
Case Presentation
Patient Profile
Mr. Sarwar Ali Khan, a 57-year-old male with a significant history of tobacco chewing, presented to Dr. Prasanta Kumar Dash, Medical Oncologist at Burjeel Specialty Hospital, with a chief complaint of a non-healing ulcer on the left side of his cheek that had been present for approximately 12 months. The patient worked as a driver for a government organization in Dubai.
Clinical Findings
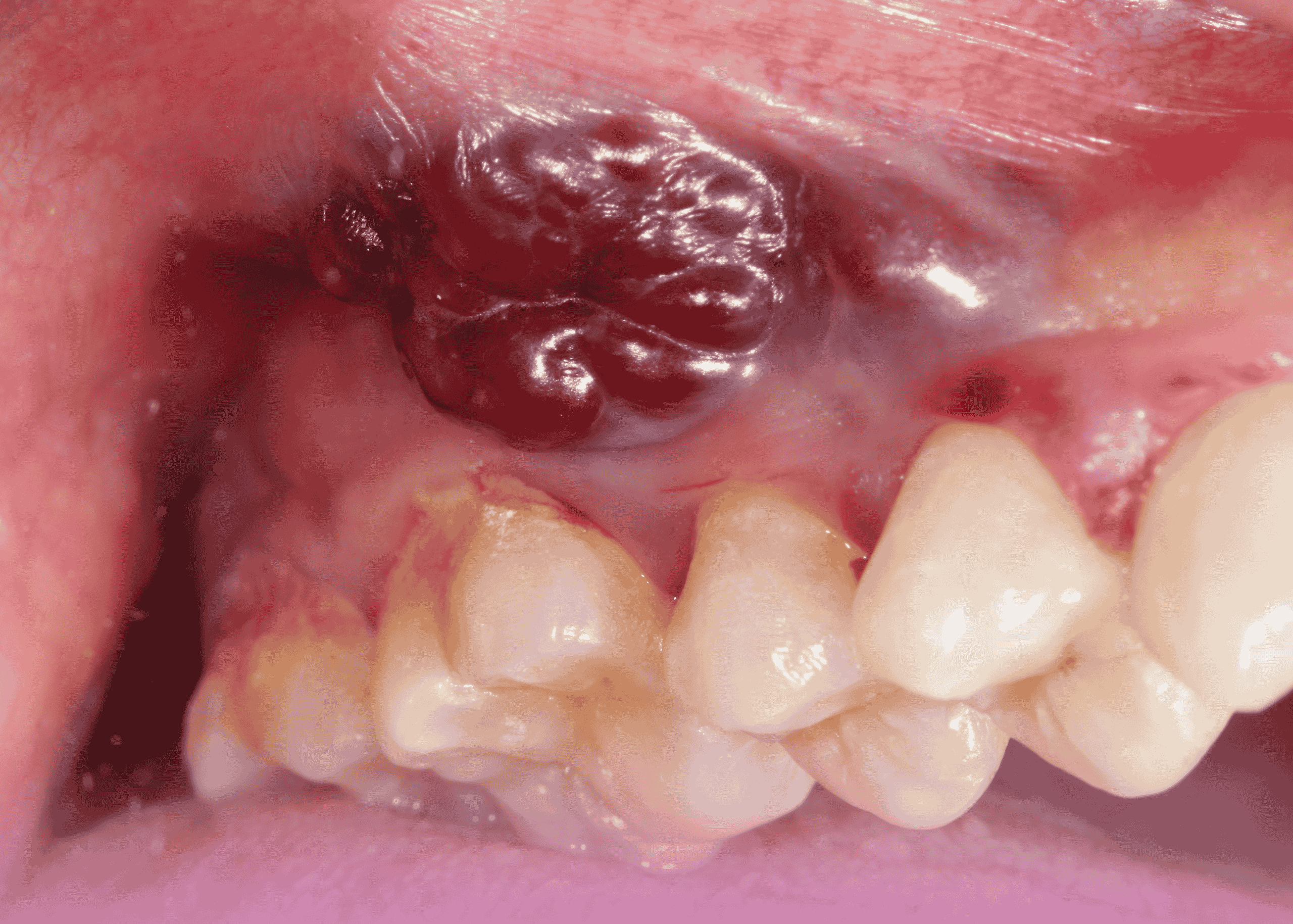
Physical examination revealed:
- A locally advanced cancerous lesion invading the lower jaw bone and involving the overlying skin
- The lesion measured approximately 3×3 cm
- A discharging sinus was present on the left side of the cheek
- No clinically palpable significant lymphadenopathy
Diagnostic Workup
The following investigations were performed:
- Biopsy: Revealed moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma
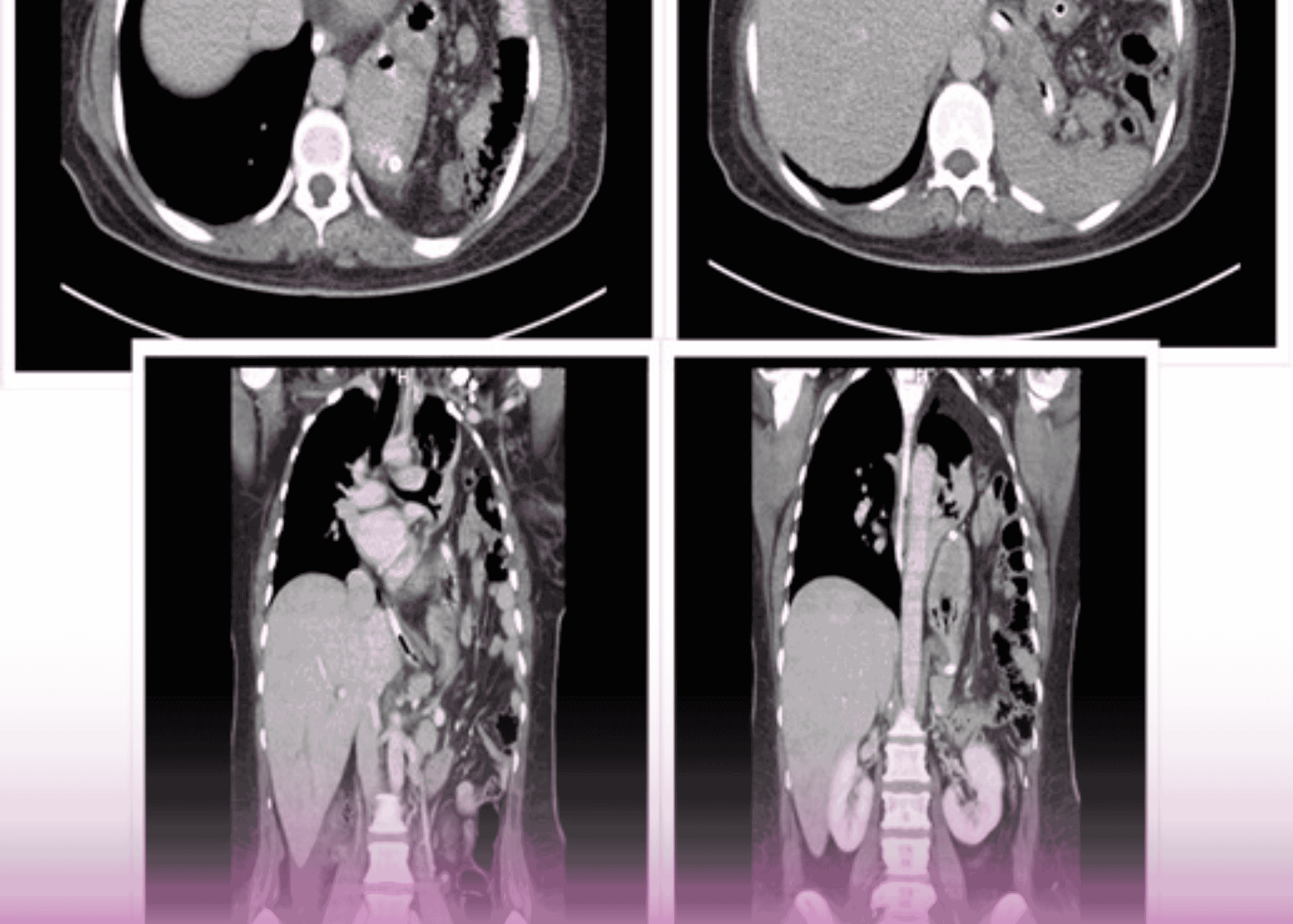
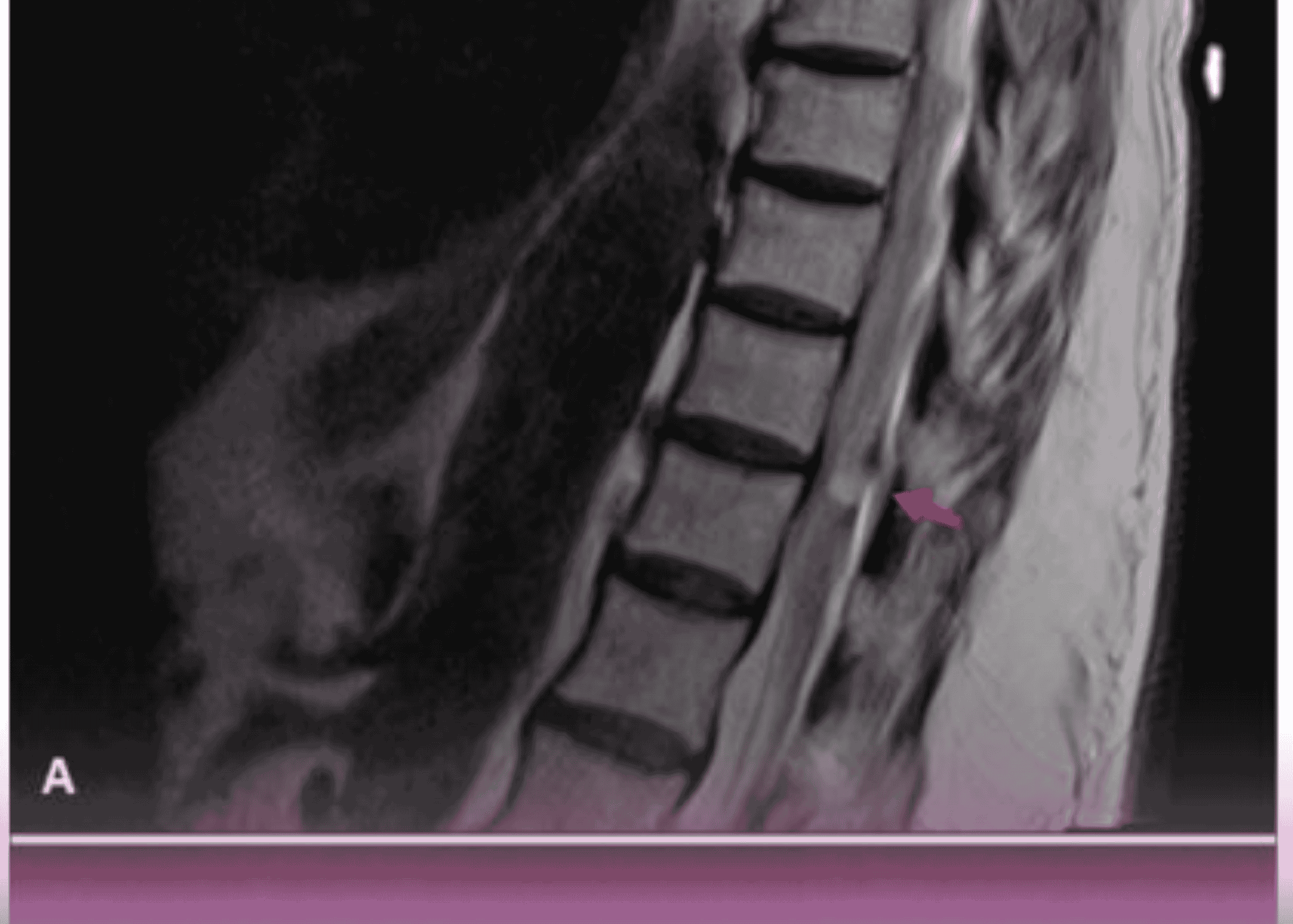
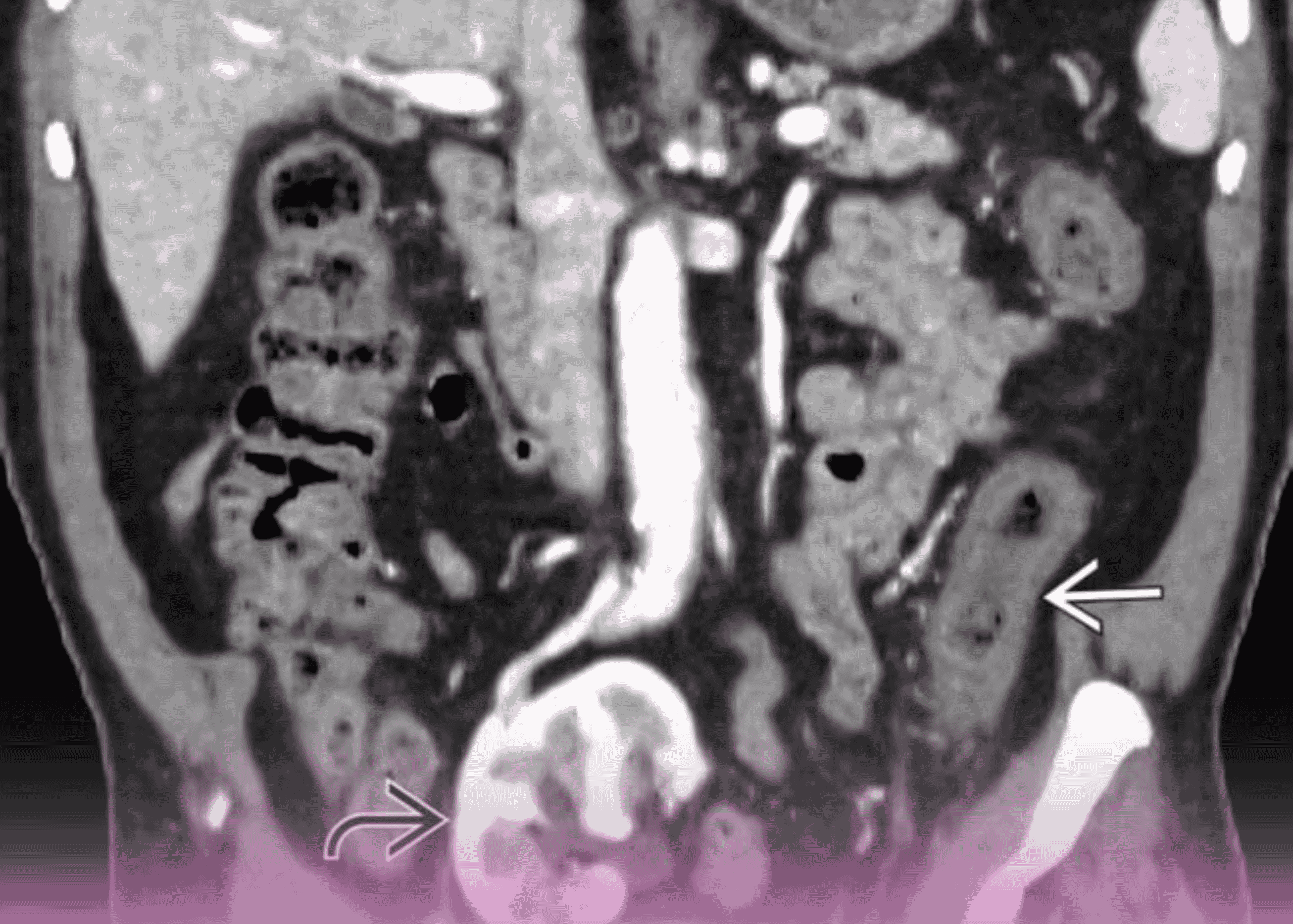
- Contrast-Enhanced CT (CECT) scan of the neck: Confirmed the locally advanced nature of the malignancy
- PET-CT scan: Corroborated the findings of the CECT and helped rule out distant metastasis
- Previous imaging review: A CT scan performed in India three months earlier (September) showed a significantly smaller lesion, indicating rapid disease progression
Based on these findings, the patient was diagnosed with locally advanced left-sided oral cavity cancer (cT4a N1 M0) with invasion of the mandible and overlying skin.
Multidisciplinary Approach
Tumor Board Discussion
The case was presented and discussed in a multidisciplinary tumor board involving physicians and oncologists from across the Burjeel network. After thorough deliberation of the diagnostic findings and consideration of various treatment options, the board unanimously recommended proceeding with surgical resection as the primary treatment modality.
This decision was based on several factors:
- Locally advanced disease amenable to surgical resection
- Absence of distant metastasis
- The aggressive progression of the disease over a short period
- The involvement of critical structures (mandible and skin) necessitating en bloc resection
Treatment Planning
Based on the tumor board recommendation, a comprehensive surgical plan was developed that included:
- Composite resection: Involving a segment of the left mandible with wide mucosal and skin margins
- Modified radical neck dissection: On the left side to address regional lymphatics
- Microvascular free fibula flap: For bone and soft tissue reconstruction
- Consideration for adjuvant therapy: Based on final histopathological findings
This complex surgical plan required careful coordination between multiple surgical specialists, including head and neck surgeons, plastic surgeons, and anesthesiologists.
Surgical Management
Procedure Details
The surgery was performed on January 6, 2024, at Burjeel Specialty Hospital in Sharjah by a multidisciplinary team led by Dr. Mohammed Basheeruddin Inamdar, Surgical Oncologist and Dr. Rajkumar CBD, Plastic Surgeon, with support from Dr. Satish V., ENT Surgeon and Dr. Mohammed Eid Ali Anesthesiologist.
The procedure consisted of several key components:
1. Tumor Resection
A complex composite resection was performed, including:
- Segmental mandibulectomy from the left first premolar to the retromolar trigone
- Wide excision of oral mucosa with appropriate margins
- Excision of involved overlying skin
- Modified radical neck dissection on the left side
2. Microvascular Free Flap Harvest and Preparation
Simultaneously, a fibula free flap was harvested from the patient’s leg:
- The fibula bone was contoured to match the resected mandibular segment
- A skin paddle was included with the flap to replace the resected oral mucosa and external skin
- The peroneal vessels (artery and vena comitantes) were meticulously dissected for microvascular anastomosis
3. Microvascular Reconstruction
The harvested free flap was positioned and secured in the defect:
- The fibula bone was shaped and fixated to recreate the mandibular contour
- Microvascular anastomosis was performed between:
- The facial artery and peroneal artery
- Two vena comitantes and branches of the jugular veins
- These anastomoses were completed using an operating microscope with precise suturing techniques
- The soft tissue components of the flap were inset to replace the resected oral mucosa and skin
Despite the complexity of the procedure, the operation was completed successfully with a duration of approximately 11 hours and minimal blood loss (300ml). No blood transfusion was required.
Technical Challenges and Considerations
The surgical management of this case involved several significant challenges:
1. Three-Dimensional Planning
The resection and reconstruction required meticulous three-dimensional planning to ensure:
- Complete tumor removal with clear margins in all dimensions (bone, mucosa, and skin)
- Precise shaping of the fibula to match the native mandibular contour
- Appropriate positioning of the skin paddle to replace both intraoral and external defects
2. Microvascular Expertise
The success of free flap reconstruction depends critically on the technical expertise of the microsurgical team:
- Vessel selection and preparation for anastomosis
- Precise microvascular suturing under high magnification
- Ensuring adequate blood flow to the transferred tissue
- Careful positioning to prevent vessel kinking or compression
3. Aesthetic and Functional Considerations
Beyond oncological clearance, the surgical team had to address:
- Mandibular continuity for chewing function
- Oral competence for speech and swallowing
- External facial appearance
- Minimal donor site morbidity
Outcomes and Follow-up
Immediate Postoperative Course
The patient’s immediate postoperative course was uneventful, with:
- Stable vital signs
- Good flap perfusion
- Appropriate pain control
- No evidence of complications
Histopathological Findings
The final histopathology report confirmed:
- Moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma
- Clear surgical margins
- Lymph node status consistent with preoperative staging
Long-term Prognosis
The complete resection with clear margins provides the patient with the best chance for long-term survival and disease control. Following this type of comprehensive surgical management, patients typically undergo:
- Regular clinical follow-up to monitor for recurrence
- Adjuvant therapy if indicated by pathological findings
- Rehabilitation for speech and swallowing as needed
- Dental rehabilitation in preparation for potential implants
Discussion
Significance of the Case
This case exemplifies several important aspects of contemporary head and neck cancer management:
1. Integrated Multidisciplinary Care
The successful outcome resulted from seamless collaboration between:
- Medical oncology for initial assessment and staging
- Surgical oncology for tumor resection
- Plastic surgery for complex reconstruction
- Anesthesiology for perioperative management
- Pathology for diagnostic confirmation and margin assessment
This integrated approach ensures comprehensive patient care from diagnosis through treatment and rehabilitation.
2. Advanced Reconstructive Techniques
The use of microvascular free tissue transfer represents the gold standard for complex head and neck reconstruction:
- Fibula free flaps provide both bone for mandibular reconstruction and soft tissue for mucosal/skin replacement
- Vascularized bone has superior healing properties compared to non-vascularized grafts
- The robust blood supply allows for better healing in previously irradiated fields
- Long-term outcomes show better functional and aesthetic results compared to other reconstructive methods
3. Evolving Standards of Care
This case reflects current best practices in advanced oral cancer management:
- Primary surgical resection for operable disease
- Immediate reconstruction to restore form and function
- Consideration of quality of life alongside oncological outcomes
- Risk-adapted adjuvant therapy based on pathological findings
Broader Clinical Implications
This case has several important implications for the broader field of head and neck oncology:
1. Importance of Early Detection
The rapid progression of this patient’s disease over just three months underscores the critical importance of early detection and intervention in oral cavity cancers. Public health initiatives focused on:
- Awareness of oral cancer signs and symptoms
- Regular dental examinations with oral cancer screening
- Education about risk factors, particularly tobacco cessation
- Prompt biopsy of suspicious oral lesions
Could significantly improve outcomes by facilitating diagnosis at earlier, more treatable stages.
2. Accessibility of Advanced Care
The successful execution of this complex procedure at Burjeel Specialty Hospital in Sharjah demonstrates the growing accessibility of advanced surgical techniques in the region. This has important implications for:
- Patient retention within regional healthcare systems
- Reduction in medical tourism for complex care
- Development of local surgical expertise and training opportunities
- Overall improvement in regional cancer care standards
3. Technical Advancement in Reconstructive Surgery
The integration of microvascular techniques into head and neck reconstruction represents a significant technical advancement that has revolutionized outcomes for patients with advanced disease:
- Before free flap techniques, reconstruction options were limited and often yielded suboptimal functional and aesthetic results
- Microvascular techniques have expanded the scope of resectable disease by providing reliable reconstruction for even the most complex defects
- Continued refinement of these techniques promises even better outcomes in the future
Future Directions
Technological Advancements
Several emerging technologies may further enhance the management of complex oral cavity cancers:
1. Virtual Surgical Planning
Computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology allows for:
- Precise preoperative planning of resection and reconstruction
- Custom cutting guides for both mandible resection and fibula osteotomies
- Patient-specific reconstruction plates that perfectly match the planned reconstruction
- Reduced operating time and improved accuracy
2. Intraoperative Navigation
Similar to GPS systems in vehicles, surgical navigation enables:
- Real-time tracking of instruments relative to the patient’s anatomy
- Enhanced precision in tumor resection
- Verification of reconstruction accuracy
- Especially valuable in complex three-dimensional reconstructions
3. Advances in Flap Monitoring
Newer technologies for postoperative flap monitoring include:
- Implantable Doppler probes for continuous blood flow assessment
- Near-infrared fluorescence angiography for real-time perfusion evaluation
- Smartphone-based photoplethysmography for nurse-driven monitoring
- These technologies can enable earlier detection of vascular compromise and improve flap salvage rates
Treatment Paradigms
Evolving treatment paradigms in oral cancer management include:
1. De-intensification Strategies
For appropriately selected patients:
- Reduction in the extent of surgery when possible
- Selective neck dissection approaches
- Risk-stratified adjuvant therapy
- These approaches aim to maintain oncological outcomes while reducing treatment-related morbidity
2. Immunotherapy Integration
The role of immunotherapy in head and neck cancer continues to evolve:
- Currently established in recurrent/metastatic disease
- Emerging data for neoadjuvant and adjuvant applications
- Potential for combination with conventional treatments
- May ultimately change the treatment landscape for advanced oral cancers
Conclusion
This case of locally advanced oral cavity cancer successfully managed at Burjeel Specialty Hospital in Sharjah exemplifies the power of multidisciplinary collaboration and advanced surgical techniques in addressing complex oncological challenges. The combination of radical tumor resection and sophisticated microvascular reconstruction enabled both cancer control and functional rehabilitation for a patient with aggressive disease.
The case highlights the importance of timely intervention, comprehensive treatment planning, and technical expertise in achieving optimal outcomes. It also demonstrates the growing accessibility of world-class cancer care within the UAE, reducing the need for patients to travel abroad for complex procedures.
For healthcare providers, this case underscores the value of specialized training in advanced surgical techniques and the benefits of multidisciplinary tumor boards in treatment planning. For patients with advanced oral cancers, it offers hope that even extensive disease can be effectively treated with approaches that prioritize both oncological clearance and functional reconstruction.
As technologies and treatment paradigms continue to evolve, the management of complex head and neck cancers will likely become even more refined, potentially leading to improved survival rates and quality of life for affected patients.