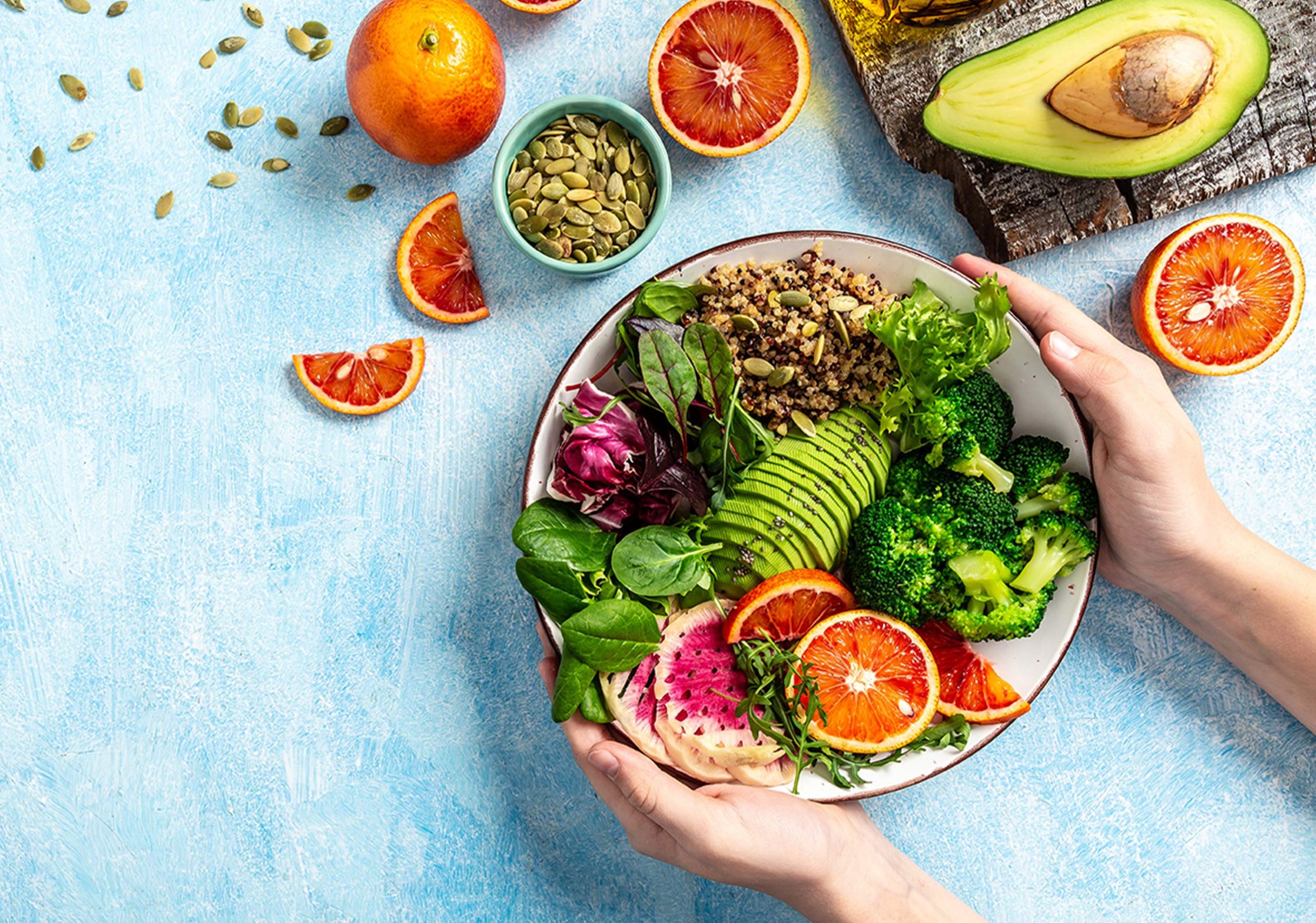
“You are what you eat”—this timeless saying holds more truth than ever in modern nutrition science. Functional foods offer health benefits that go beyond basic nutrition, playing an active role in preventing disease and promoting overall wellness.
What Are Functional Foods?
Functional foods are nutrient-rich foods containing bioactive compounds – natural substances that provide specific health benefits beyond basic nutritional value. These include polyphenols, omega-3 fatty acids, probiotics, prebiotics, and various vitamins and minerals that work actively in your body.
Unlike regular foods that simply provide calories and nutrients, functional foods:
- Boost your immune system naturally
- Improve digestion and support gut health
- Protect your heart and brain function
- Enhance sleep quality and duration
- Reduce inflammation throughout your body
Best Functional Foods for Gut Health, Immunity, and Better Sleep
Choosing the right functional foods can address your specific health needs:
| Benefit | Foods | Why They Work |
| Gut Health | Yogurt, kefir, oats, high-fiber vegetables | Probiotics & fiber support digestion and gut microbiome |
| Immunity | Berries, leafy greens, nuts, seeds | Antioxidants & vitamins strengthen natural defenses |
| Better Sleep | Almonds, walnuts, fatty fish, chamomile | Melatonin, magnesium, omega-3s promote restful sleep |
Understanding the Gut Microbiome Connection
Your gut microbiome—the community of beneficial bacteria in your digestive system—plays a central role in overall health.
Probiotic foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi introduce beneficial bacteria directly into your gut, helping maintain digestive balance, strengthen immunity, and even influence mood and mental clarity.
Prebiotic foods such as oats, bananas, garlic, onions, and high-fiber vegetables provide fuel for your existing beneficial bacteria, creating a thriving internal ecosystem that supports everything from nutrient absorption to disease prevention.
Key Health Benefits of Functional Foods
Incorporating functional foods into your diet delivers wide-ranging improvements:
- Helps prevent chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and obesity
- Strengthens immunity and supports natural defences
- Improves digestion and gut health
- Boosts energy levels and mental clarity
- Promotes better sleep and recovery
How to Incorporate Functional Foods into Your Daily Diet Plan
Making functional foods part of your routine doesn’t require a complete dietary overhaul. Small, consistent changes make a significant impact.
Healthy Breakfast Swaps
Functional foods for steady energy
- Overnight oats + probiotic yogurt, berries, chia
- Greek yogurt parfait + seeds, nuts, berries
- Whole-grain toast + avocado, smoked salmon
- Smoothie bowl + greens, berries, flax, almond butter
Mid-Day Functional Snacks
Light, filling, and nutrient-rich
- Mixed nuts and seeds for omega-3s and magnesium
- High-fiber vegetables with hummus for prebiotic fiber
- Fresh berries or kiwi for antioxidants and vitamin C
- Dark chocolate (70% cacao or higher) for polyphenols
Balanced Diet Plan Framework
Build every meal with these
- Whole grains: oats, quinoa, brown rice
- Lean proteins: fish, poultry, legumes, eggs
- Omega-3s: salmon, walnuts, flax, chia
- Colorful produce: fruits & vegetables
- Probiotics: yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut
Your nutritional needs are unique. At Burjeel by the Beach Clinic, our team will create personalized diet plans based on your health, goals, and lifestyle.
Ready to transform your health?
Book a consultation today and start your functional food journey with expert guidance.
Your Journey to Better Health Starts Here
Transforming your health through functional foods is a powerful step toward long-term wellness, but optimal nutrition is most effective when tailored to your individual needs. Whether you’re managing chronic conditions, seeking preventive care, or simply wanting to optimize your overall health, personalized medical guidance makes all the difference.
At Burjeel by the Beach Saadiyat, our experienced Internal Medicine specialists work alongside nutrition experts to provide comprehensive, patient-centered care. We take the time to understand your unique health profile, medical history, and wellness goals to create customized diet plans and treatment strategies that work for you—not just in theory, but in your daily life.
From managing digestive concerns and metabolic health to addressing chronic inflammation and immunity challenges, our integrated approach ensures that your nutrition plan aligns seamlessly with your overall medical care.
Ready to transform your health with expert guidance?
Book a consultation with our Internal Medicine specialists at Burjeel by the Beach Saadiyat today and discover how functional foods can become a cornerstone of your personalized wellness journey.
Book your appointment and take the first step toward a healthier, more vibrant you.