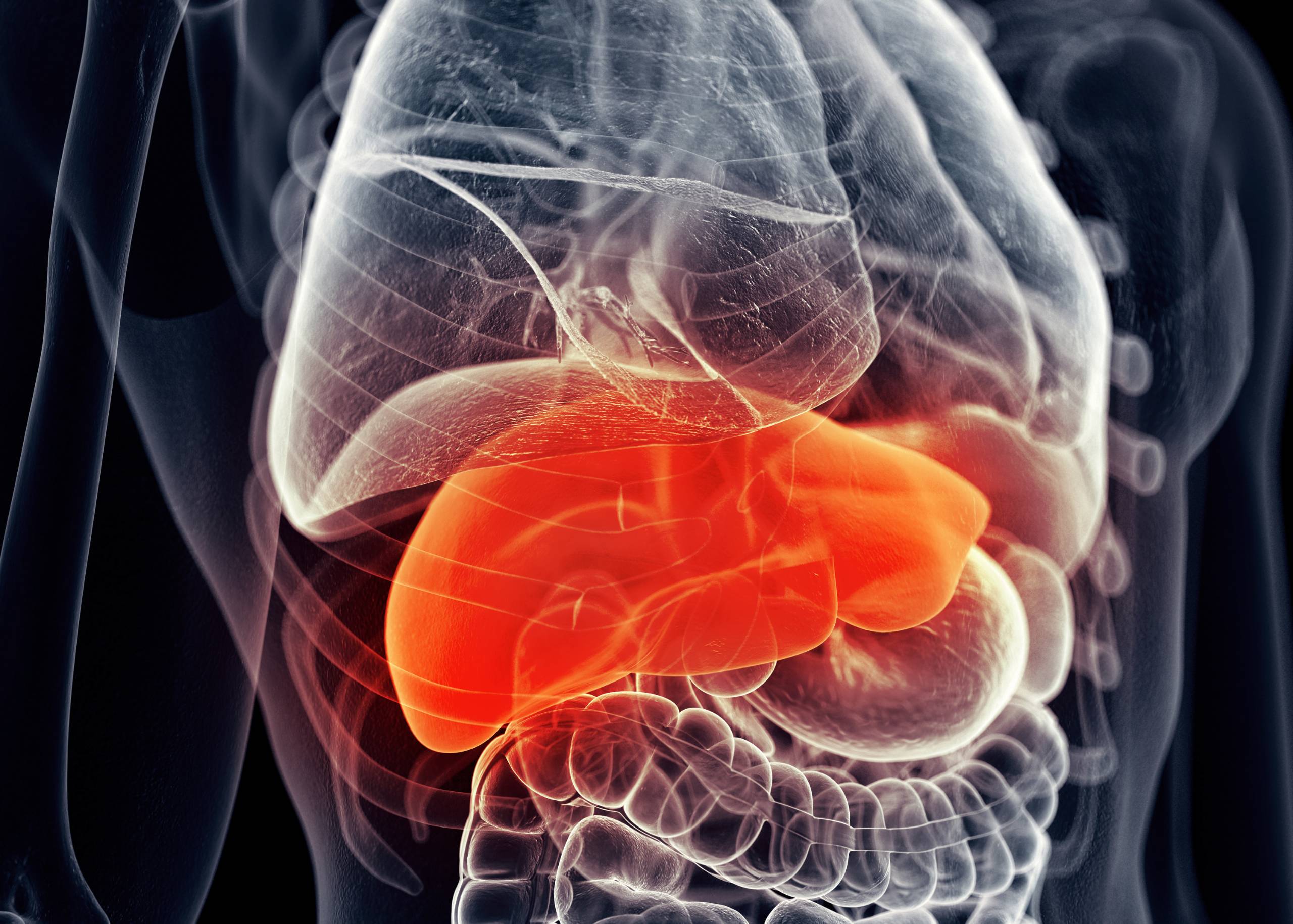
Liver cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancerous) cells form in the liver. The word “liver” can also refer to other abdominal organs that perform similar functions, including the gallbladder, stomach, and pancreas. Liver cancer may also be called hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which means “cancer of the liver.” The liver is a large gland in the upper right of the abdomen. It performs many functions, including detoxifying blood, producing bile to help digest fats, and storing vitamins A and D. The liver also helps regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels by converting excess glucose into glycogen for storage in muscles or fat cells.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer
The symptoms depend on the stage of cancer. In general, symptoms include:
- Vomiting (nausea) or feeling like you can’t keep anything down
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, and whites of the eyes)
- Loss of appetite or weight loss -Fatigue or weakness
Causes of Liver Cancer
A number of different factors causes liver cancer. Some of these include:
- Hepatitis B and C infections
- Liver diseases, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis
- Alcohol abuse
- Cigarette smoking
- Obesity
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection accounts for about one-third of all cases of HCC worldwide and about 70% in Asia. Other causes include hepatitis C virus (HCV), cirrhosis due to alcohol abuse, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Diagnosis
It is diagnosed with imaging, blood tests, and biopsies. Imaging can be done with ultrasound, CT, MRI, or PET scans.
- An ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce an image of the liver on a monitor.
- CT scans use X-rays to create three-dimensional images of internal structures. MRIs use radio waves and magnetic fields to generate images of the body’s internal structures.
- PET scans use a small amount of radioactive material that attaches itself to cancer cells so the scanner can detect them.
- Blood tests check for certain proteins in the blood that may indicate cancerous tissue growth. These proteins include AFP (alpha fetoprotein), CA 19–9 (carbohydrate antigen 19–9), and CA 72–4 (carbohydrate antigen 72–4).
- Biopsies are performed on the liver tissue to confirm whether or not cancer is present.
Treatment
Liver cancer is a serious disease that can be fatal if not treated. The main goal of treatment is to cure cancer, but this may not always be possible. Treatment options depend on the type and stage of your liver cancer.
The main treatment options for early-stage liver cancer include surgery and chemotherapy.
Surgery may include a partial hepatectomy (removing part of your liver) or a liver transplant.
More advanced tumors may require chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Liver transplantation is an option for patients who have a liver tumor that cannot be removed by surgery or when their tumors have spread to other parts of their body. The surgery involves removing the patient’s diseased liver and replacing it with a healthy one from another person or donor organ.
Experts in the Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery and Transplantation at Burjeel Medical City (BMC), Abu Dhabi, treats patients suffering from liver, pancreas, and biliary system ailment.
Liver Cancer & Transplant Expert

Dr. Rehan Saif
Director of Transplant Surgery for Burjeel Abdominal Multi-Organ Transplant Program, Clinical Lead HPB Surgery, Consultant General Surgery