Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness worldwide, especially among people over 60. The challenge with this condition is that it often develops silently — without noticeable warning signs — until vision loss has already occurred.
This comprehensive guide explains the glaucoma symptoms, early indicators, risk factors, diagnosis methods, and treatment options to help you protect your vision and maintain lifelong eye health.
What is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma refers to a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, the part of the eye responsible for sending visual information to your brain. This damage is usually caused by increased intraocular pressure (eye pressure), although glaucoma can sometimes occur even when eye pressure is normal.
Over time, the pressure damages the optic nerve fibers, leading to gradual — and often permanent — vision loss.
There are several types of glaucoma, but the two most common are primary open-angle glaucoma and angle-closure glaucoma.
Glaucoma Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms of glaucoma vary depending on the type and stage of the disease. Some forms progress so slowly that you might not notice vision changes until significant damage has occurred.
1. Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Symptoms
This is the most common type of glaucoma. It develops gradually and painlessly, which makes it easy to overlook in the early stages.
Typical symptoms include:
- Gradual loss of peripheral (side) vision, usually in both eyes
- Tunnel vision in advanced stages
- No pain or discomfort despite ongoing optic nerve damage
Because symptoms appear slowly, regular eye exams are the only reliable way to detect open-angle glaucoma early.
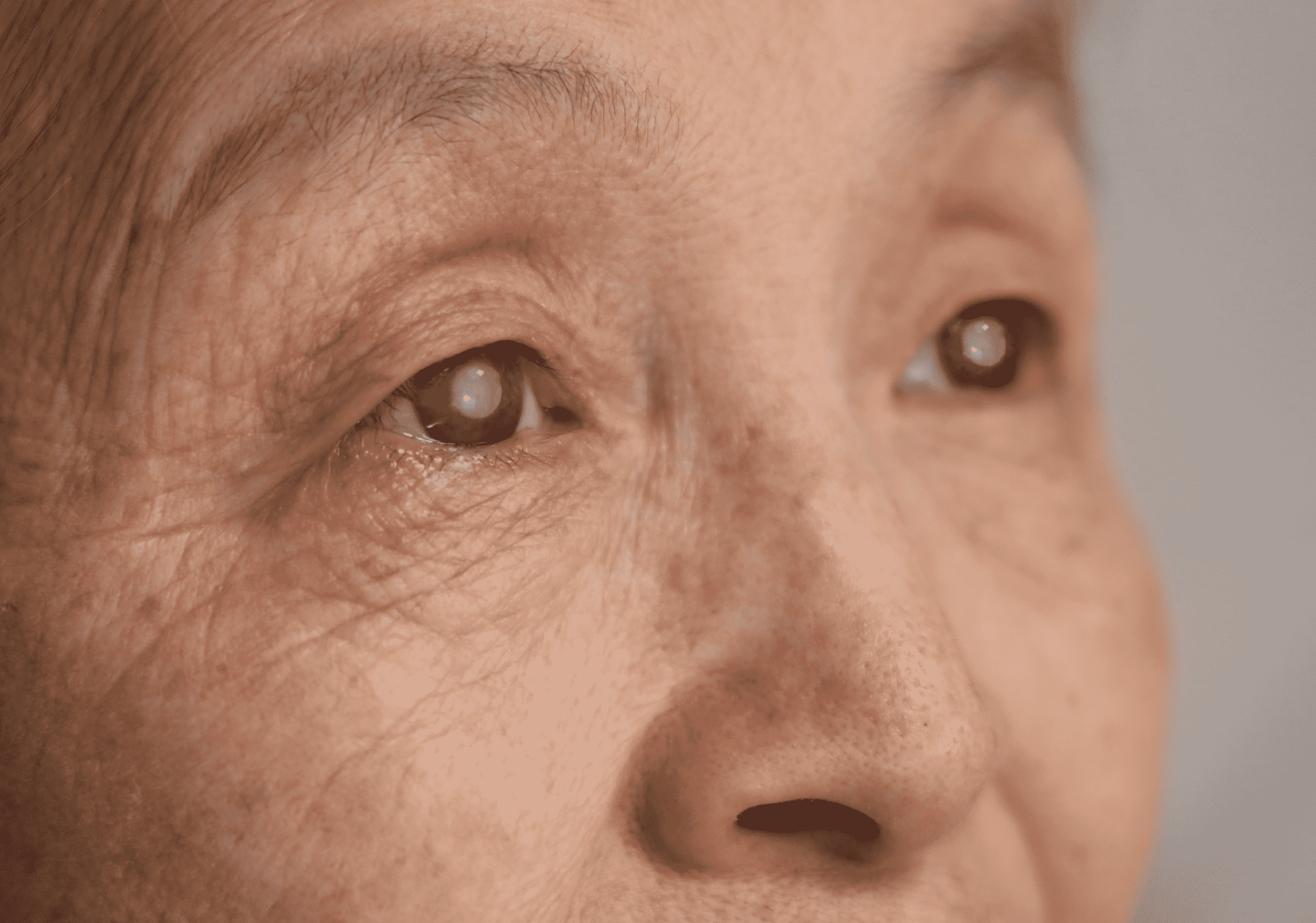
2. Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma Symptoms
Unlike open-angle glaucoma, acute angle-closure glaucoma is a medical emergency that occurs suddenly when the drainage angle in the eye becomes completely blocked.
Symptoms include:
- Severe eye pain and headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sudden blurred vision
- Halos or rainbows around lights
- Redness in the eye
If you experience these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention — untreated acute glaucoma can cause permanent blindness within days.
Risk Factors for Glaucoma
Anyone can develop glaucoma, but certain factors increase your risk:
- Age: Risk increases after age 60.
- Family History: Genetics play a significant role in glaucoma development.
- Ethnicity: African, Asian, and Hispanic populations are at higher risk.
- Medical Conditions: Diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease can raise your risk.
- Eye Injuries or Surgery: Trauma or past eye surgeries can increase vulnerability.
- Long-Term Steroid Use: Extended use of corticosteroids can elevate eye pressure.
Knowing these risk factors can help you take preventive action, such as scheduling regular comprehensive eye exams.
How is Glaucoma Diagnosed?
Because glaucoma often develops without early symptoms, routine eye exams are essential for early detection. A complete glaucoma evaluation typically includes:
- Tonometry: Measures intraocular pressure.
- Ophthalmoscopy: Examines the optic nerve for signs of damage.
- Perimetry (Visual Field Test): Detects blind spots or peripheral vision loss.
- Gonioscopy: Inspects the drainage angle of the eye.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): Provides detailed images of the optic nerve and retina.
Early diagnosis is the best defense against permanent vision loss.
Treatment for Glaucoma
Although vision lost to glaucoma cannot be restored, treatment can slow or stop further damage. Your ophthalmologist will recommend the best approach based on your specific condition and stage.
Common treatments include:
- Prescription Eye Drops: Help lower intraocular pressure.
- Oral Medications: Used if eye drops alone are insufficient.
- Laser Therapy: Improves fluid drainage in the eye.
- Surgery: In advanced cases, surgical procedures can create new drainage pathways or reduce fluid production.
Consistent follow-up care is crucial to monitor progress and prevent further optic nerve damage.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) What are the first signs of glaucoma?
The earliest sign is usually a subtle loss of side (peripheral) vision. Many people don’t notice it until significant damage has occurred, which is why regular check-ups are vital.
2) Can glaucoma symptoms come and go?
No. Glaucoma damage is progressive and permanent. Symptoms may worsen gradually over time without treatment.
3) How long does it take to go blind from glaucoma?
Without treatment, glaucoma can cause blindness in several years. However, with proper care and regular monitoring, most patients retain useful vision for life.
Conclusion
Recognizing glaucoma symptoms early can make the difference between preserving your vision and losing it permanently. Because the disease often develops silently, regular comprehensive eye exams are your best protection.
If you notice vision changes or have risk factors for glaucoma, don’t delay — schedule an appointment with an eye specialist today.
Protect your vision with early intervention. If you’re experiencing symptoms or are at risk, consult one of our expert Ophthalmologists at Burjeel Specialty Hospital, Sharjah, and schedule a comprehensive eye examination today.