An ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) tear is one of the most common and serious knee injuries, especially among athletes and physically active individuals. Whether caused by sudden twisting, pivoting, or impact, this injury can significantly affect mobility, stability, and quality of life. Understanding the ACL tear recovery process — including surgical and non-surgical options — helps patients make informed decisions about their knee injury treatment.
At Burjeel Hospital Sharjah, orthopedic specialists provide personalized treatment plans based on injury severity, activity level, and long-term goals.
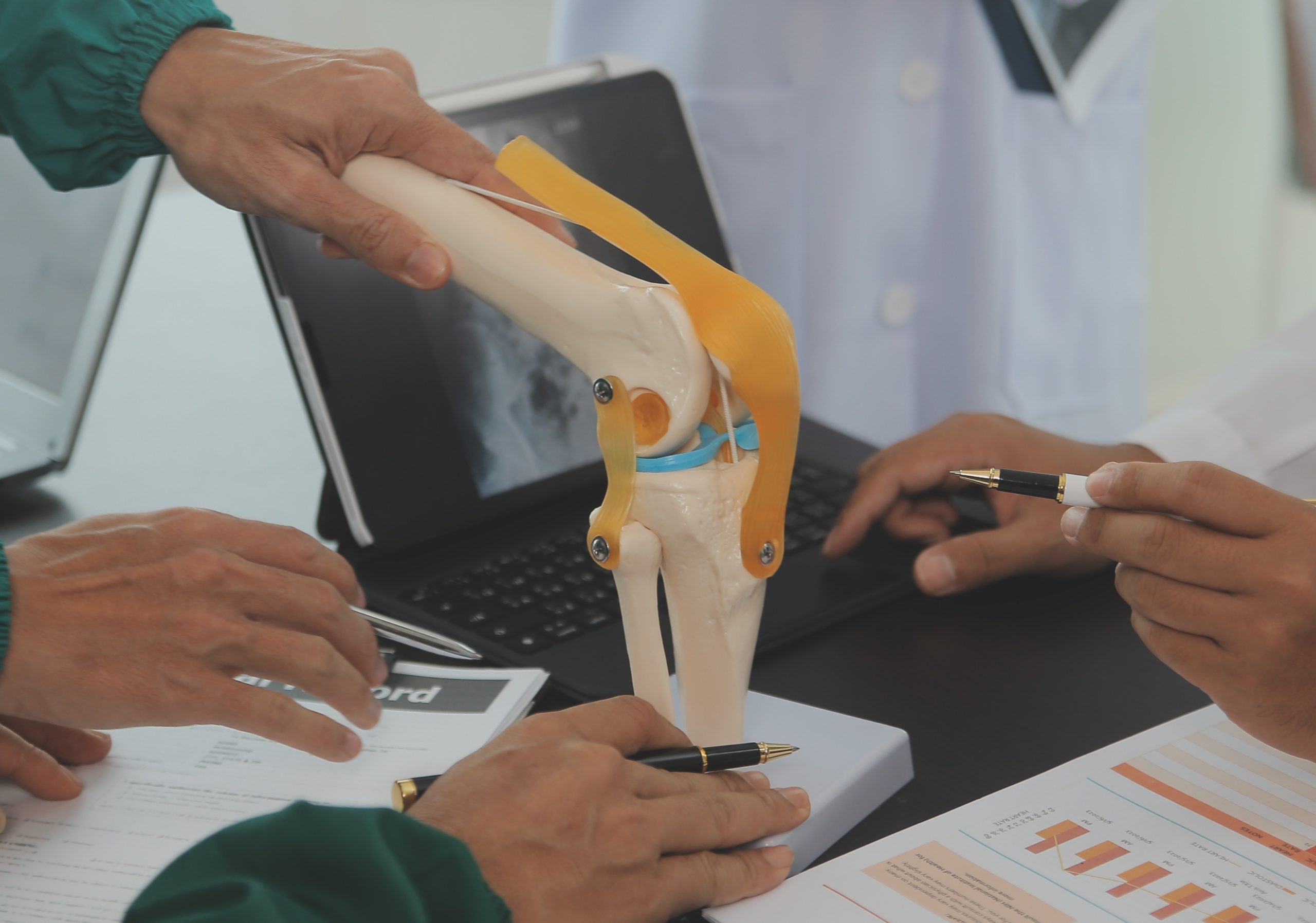
What is an ACL Tear?
The ACL is a key ligament that stabilizes the knee joint by connecting the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). It prevents excessive forward movement and rotation of the knee.
Common Causes
- Sudden stops or direction changes
- Pivoting movements
- Jumping and landing incorrectly
- Direct blows to the knee (sports or accidents)
ACL tears are classified as:
- Grade 1: Mild stretching
- Grade 2: Partial tear
- Grade 3: Complete rupture
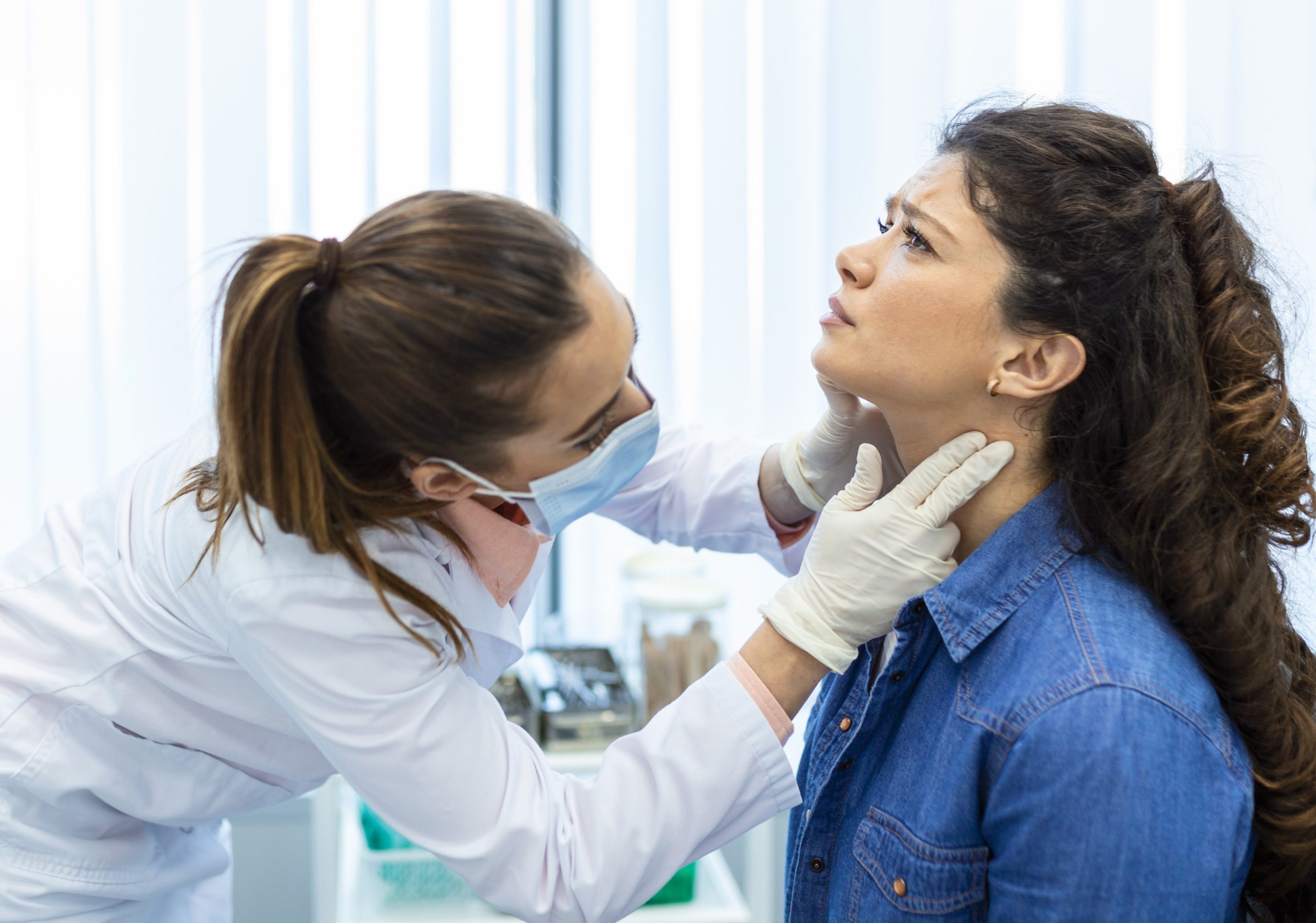
Symptoms of an ACL Tear
Typical signs include:
- A “popping” sensation at the time of injury
- Immediate pain
- Rapid swelling
- Knee instability or “giving way”
- Reduced range of motion
- Difficulty bearing weight
Prompt medical evaluation is essential to confirm diagnosis and prevent further damage.
Non-Surgical Treatment: Who Is It For?
Not all ACL injuries require surgery. Conservative management may be appropriate for:
- Partial tears
- Individuals with low physical demands
- Older adults
- Patients willing to avoid high-impact activities
Non-Surgical Knee Injury Treatment Options
- Physical therapy to strengthen surrounding muscles
- Knee bracing for stability
- Activity modification
- Pain management and anti-inflammatory medication
Non-Surgical ACL Tear Recovery Timeline
- Weeks 1–2: Reduce swelling and pain, begin gentle movement
- Weeks 3–6: Strengthening exercises and improved mobility
- Weeks 7–12: Advanced rehabilitation and balance training
- 3–6 months: Gradual return to normal daily activities
However, instability may persist, especially during sports or strenuous activities.
ACL Surgery: When Is It Recommended?
Surgical reconstruction is often advised for:
- Complete ACL tears
- Athletes or highly active individuals
- Knee instability affecting daily life
- Associated injuries (meniscus or cartilage damage)
- Failure of conservative treatment
ACL surgery typically involves replacing the torn ligament with a graft from the patient’s own tissue or a donor.
ACL Surgery Timeline and Recovery
Recovery after reconstruction is longer but often restores stability and function more effectively.
ACL Surgery Timeline
First 2 Weeks
- Pain control and swelling reduction
- Use of crutches and knee brace
- Gentle range-of-motion exercises
Weeks 3–6
- Gradual weight-bearing
- Physical therapy focusing on mobility and strength
Weeks 7–12
- Increased strengthening and balance training
- Improved walking pattern
3–6 Months
- Return to light sports or physical activities
- Advanced rehabilitation
6–12 Months
- Full return to competitive sports (in most cases)
Strict adherence to rehabilitation protocols is essential for successful recovery.
Surgery vs. Non-Surgical Treatment: Key Differences
| Aspect | Non-Surgical Treatment | ACL Surgery |
| Recovery Time | 3–6 months | 6–12 months |
| Knee Stability | May remain limited | Usually restored |
| Return to Sports | Often restricted | Typically possible |
| Risk of Re-Injury | Higher | Lower with proper rehab |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive | Surgical procedure |
Your orthopedic specialist will help determine the most appropriate approach based on your goals and lifestyle.
Long-Term Outlook
With proper treatment and rehabilitation, many individuals regain excellent knee function. However, untreated instability may increase the risk of additional injuries or early osteoarthritis.
FAQs
1. Can an ACL tear heal without surgery?
Partial tears may heal with rehabilitation, but complete tears usually do not heal on their own.
2. Is ACL surgery painful?
Post-operative discomfort is expected but manageable with medication and therapy.
3. When can I walk after ACL surgery?
Most patients begin walking with support within a few days to weeks, depending on progress.
4. Can I return to sports after ACL reconstruction?
Yes, many patients return to sports within 6–12 months with proper rehabilitation.
5. What happens if I don’t treat an ACL tear?
Untreated tears can lead to chronic instability, meniscus damage, and long-term joint problems.
Conclusion
An ACL tear can be a life-altering injury, but effective treatment options are available. Understanding the ACL tear recovery process — whether through conservative management or surgical reconstruction — helps patients choose the best path for their lifestyle and goals. While non-surgical approaches may suit less active individuals, surgery often provides superior stability for those wishing to return to high-level physical activity.
Early evaluation and personalized care are key to achieving the best outcome.
Comprehensive Knee Care at Burjeel Hospital Sharjah
At Burjeel Hospital Sharjah, our experienced orthopedic specialists offer advanced diagnostics, individualized treatment plans, and state-of-the-art rehabilitation for ACL injuries and other knee conditions.
Don’t let a knee injury hold you back.
Book your consultation today to explore the most effective treatment for your ACL tear. Call now or schedule an appointment online and take the first step toward recovery and confident movement.