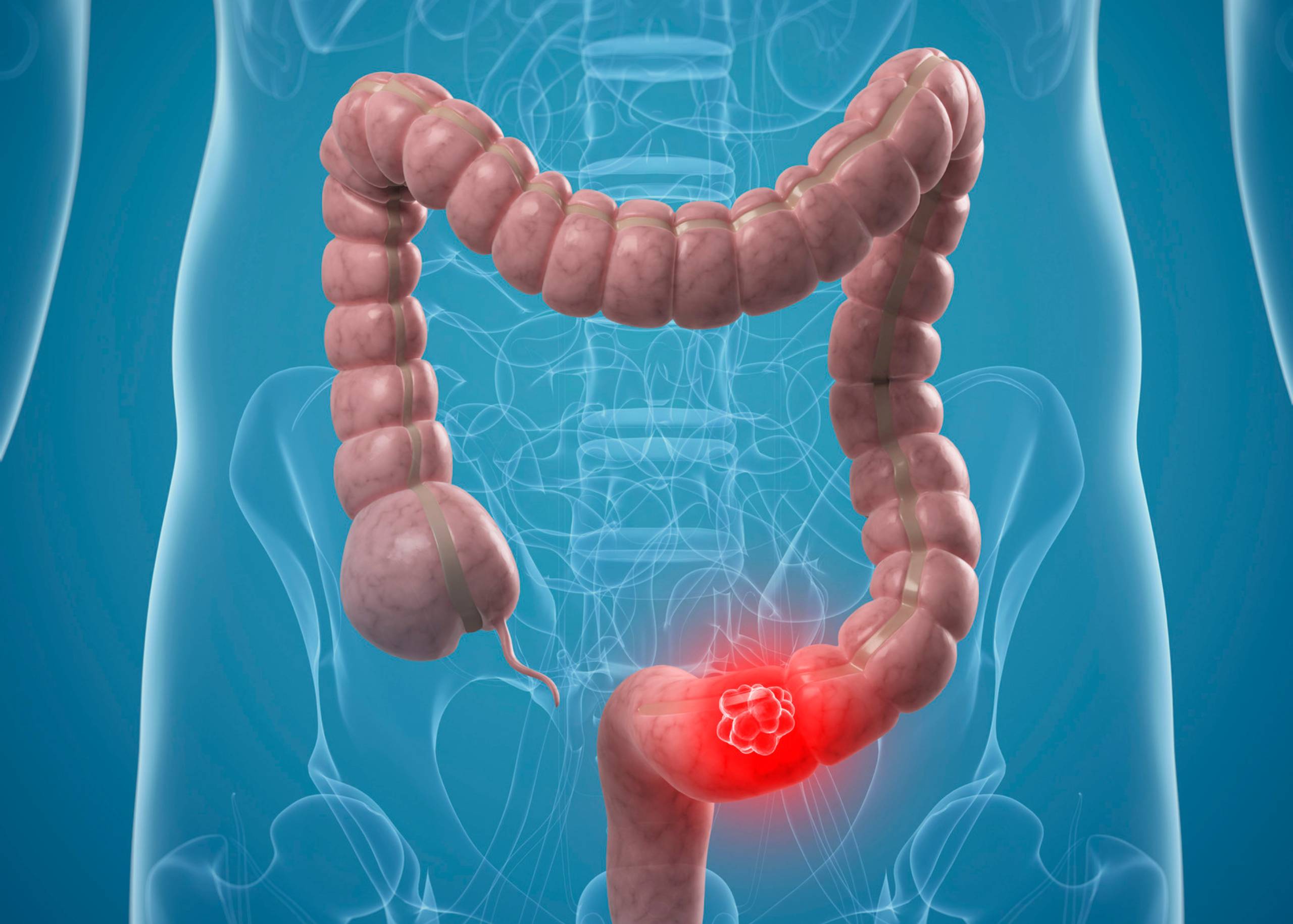
Colon cancer is a disease that affects the colon, which is the part of the digestive system between the stomach and the anus. Colon cancer can occur anywhere in the large intestine (colon) or rectum. The colon is responsible for absorbing fluids from foods and turning them into waste. The most common type of colon cancer begins in cells lining the large intestine’s inner surface. This type of cancer is called adenocarcinoma, and it can start in any part of your colon. It may also affect other areas of your body, including your appendix, rectum, or blood vessels. These are called secondary cancers.
Symptoms of Colon Cancer
The symptoms include:
- Blood in the stool
- Unintended weight loss
- Persistent abdominal pain or cramps
- A feeling of fullness after eating only a small amount of food
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes are unknown, but research has shown that several factors increase your risk of developing it.
Age: Older people have a greater risk for developing colon cancer. This is because our bodies become less able to fight off germs and other things that can cause cancer as we age.
Gender: Men and women have different risks for colon cancer. Men tend to develop it at a younger age than women and are more likely to have hereditary forms of the disease. Women are more likely to develop colon cancer from environmental factors such as diet or lifestyle choices like smoking cigarettes and drinking alcohol heavily over many years, which can lead to chronic inflammation in the body (inflammation increases your risk for most types of cancer).
Family History: If your parents or other close relatives had colon cancer, you might be more likely to develop it yourself. Having Lynch syndrome (a genetic condition) also increases your risk of developing colorectal cancers because it causes changes in DNA repair genes that damage chromosomes over time, making cells more likely to divide uncontrollably when they shouldn’t be dividing.
Genetic Mutations: The genes that control cell growth may be damaged by aging or exposure to chemicals. These changes may cause cells to grow in an uncontrolled way and form a tumor.
Diet: A diet high in fat and red meat has been linked to colon cancer. Dairy products may also increase your risk of developing colon cancer. Studies show that people who consume more fruits and vegetables have a lower risk of developing the disease.
Lifestyle: Some studies suggest that smoking increases your risk of developing the condition, while others have found no link between tobacco use and this type of cancer. Obesity may also increase your risk for this type of cancer by causing chronic inflammation in the body.
Diagnosis of Colon Cancer
A doctor diagnoses the condition via a physical exam, blood tests, and imaging tests. The most common method of diagnosis is a colonoscopy, an endoscope that allows the doctor to view and examine the inside of the colon. A biopsy may be taken during this procedure to confirm or rule out cancer. A fecal occult blood test (FOBT) is another common method of diagnosing the condition.
Treatment
Colon cancer is treated through surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Surgery is the most common treatment for this type fo cancer, and it involves removing the affected area of the colon through an incision made in the abdomen. This type of surgery may be performed along with other procedures to remove any tumors that have spread into nearby lymph nodes or tissues, such as lymphadenectomy or a resection. If the entire colon has been removed, your doctor may recommend an ostomy procedure to create an opening in your abdomen so waste can leave your body.
Chemotherapy may be used to treat the condition. It cannot be removed by surgery or if it has spread to other parts of your body. Chemotherapy uses drugs that destroy cancer cells and stop them from growing or spreading further. Radiation therapy is often used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells in your body.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target tumors and kill any remaining cancer cells.
At Burjeel Medical City, our expert team of gastroenterologists, gastrointestinal surgeons, general and laparoscopic surgeons and oncologists provide treatment for colon cancer. We offer a range of treatments, from minimally invasive surgery to chemotherapy and radiation therapies. Our team can help you manage the symptoms of your condition and ensure that you receive the best possible treatment plan for your situation. We understand that dealing with colon cancer can be overwhelming, but we are here to guide you through each step.
Our General and Laparoscopic Surgeons