Burjeel Medical City has successfully implemented an innovative, minimally invasive approach to treating cerebral cavernous vascular malformations, offering new hope for patients with this challenging neurological condition.
Understanding the Patient’s Journey
A 23-year-old male patient presented with a history of cerebral cavernous vascular malformation diagnosed approximately one year prior. His condition was initially discovered following a seizure episode with loss of consciousness that required ICU admission. Initial MRI revealed a left frontal hematoma, which was managed conservatively with anti-epileptic medications.
Two weeks prior to his presentation at Burjeel Medical City, the patient experienced a recurrence of symptoms following an episode of hypertension. Upon examination, he was fully conscious with no neurological deficits, but required a comprehensive evaluation to prevent further episodes.
Sophisticated Diagnostic Approach
High-resolution MRI performed at Burjeel Medical City revealed:
- Focal cortical-based altered signal intensity areas in the left temporal and left frontal lobes with enhancement measuring approximately 2.1 and 1.8 cm respectively, classified as type II Zabramski
- Multiple small centimeter to subcentimeter foci throughout the supratentorial brain parenchyma
- Additional tiny dot-like foci in the pons and left cerebellar hemisphere, classified as type IV Zabramski
These findings confirmed the diagnosis of multiple cavernous vascular malformations, with the larger lesions posing a significant risk for future bleeding events.
Multidisciplinary Treatment Approach
The neurosurgical team at Burjeel Medical City, led by Dr. Mohamed A. Elzoghby and Dr. Essam Elgamal, carefully assessed the patient’s condition in collaboration with radiology, oncology, and radiation oncology specialists through the CNS tumor board.
After thorough evaluation, the team recommended surgical intervention for the two larger lesions in the left frontal and temporal lobes. The surgical plan incorporated several advanced techniques:
- Minimally invasive craniotomies (3 cm each) precisely targeted to each malformation
- Neuronavigation guidance for pinpoint accuracy
- Continuous electrophysiological monitoring to protect critical brain functions
- Intraoperative MRI for real-time confirmation of complete resection
Surgical Challenges and Innovations
The procedure presented several unique challenges:
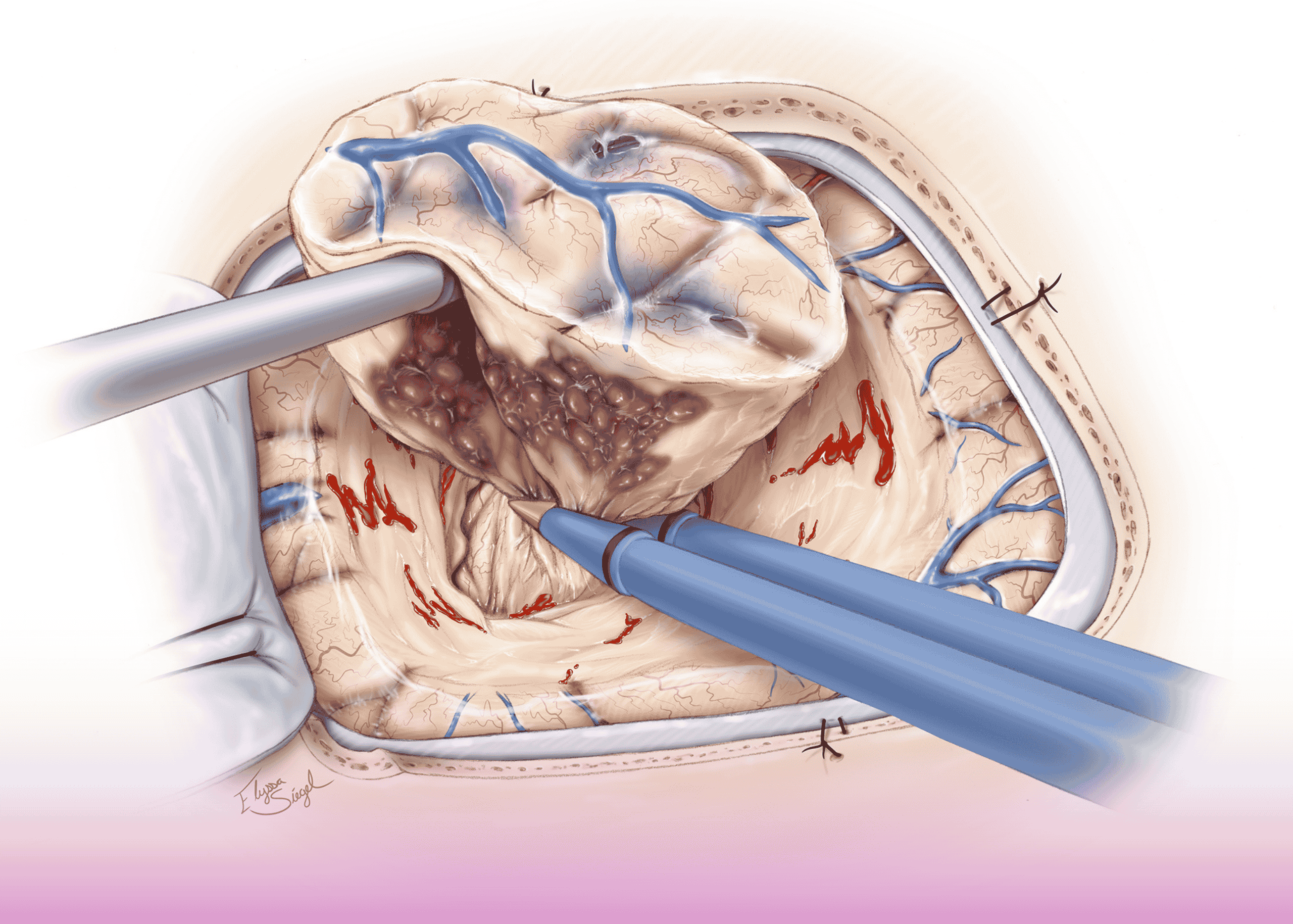
Critical Location: The lesions were located near the motor area in the dominant hemisphere, requiring exceptional precision to avoid permanent neurological deficits. One particularly delicate aspect involved a cortical artery running directly over one of the malformations, which required careful dissection and preservation.
Pathology Considerations: Cavernous malformations contain abnormally thin-walled blood vessels prone to bleeding. The surgeons utilized microsurgical techniques to meticulously remove the lesions while minimizing the risk of intraoperative hemorrhage.
During the procedure, frozen section analysis confirmed the diagnosis, and intraoperative MRI verified complete resection of both lesions without residual malformation or vascular complications.
Advancing Neurosurgical Excellence
This case exemplifies the significant advantages of combining minimally invasive surgical approaches with advanced intraoperative imaging and monitoring technologies. For patients with cavernous malformations in critical brain regions, this approach offers:
- Reduced surgical trauma
- Lower risk of neurological deficits
- Confirmation of complete resection before closure
- Improved recovery and outcomes
The multidisciplinary team also included Dr. King Jee Dhar (Anesthesiologist), Dr. Rawia Mubarak Mohamed (Anatomic Pathology), and Dr. Mohsin Saleem Basade (Radiology), highlighting Burjeel Medical City’s comprehensive approach to complex neurological conditions.