Introduction
Burjeel Hospital Abu Dhabi has successfully pioneered an innovative interventional radiology approach for treating a complex hepatic artery aneurysm. This case study highlights how creative technical solutions and advanced interventional expertise can provide life-saving treatment for potentially catastrophic vascular conditions through minimally invasive techniques.
Patient Presentation
A 32-year-old male presented to the emergency department with severe abdominal pain. Computed tomography (CT) revealed a concerning picture: hemoperitoneum (blood in the abdominal cavity) and a large aneurysmal dilation of the left hepatic artery with irregular borders and extra-luminal contrast material. While no active extravasation was visible at the time of imaging, the condition presented an immediate life-threatening risk. Notably, the scan also revealed bilateral renal artery dissections, suggesting a possible systemic vascular pathology.
Technical Challenge
The location and morphology of the hepatic artery aneurysm presented significant challenges for conventional endovascular treatment approaches. Traditional coil embolization alone risked incomplete exclusion of the aneurysm or coil migration, while standard liquid embolic agents could potentially migrate to non-target vessels, causing serious complications.
Innovative Solution
Dr. Mohamed Almarzooqi, Medical Director and Consultant Interventional Radiologist at Burjeel Hospital Abu Dhabi, devised a creative two-stage approach that combined established techniques in a novel way:
- Coil Cage Creation: Initially, a framework of embolization coils was carefully deployed to form a stable cage within the aneurysm. This framework served as both structural support and a containment system for the next phase of treatment.
- Magic Glue as Filler: Following the establishment of the coil framework, the internal volume was methodically filled with a specially prepared mixture of Magic Glue (n-butyl cyanoacrylate) and non-ionic contrast. This innovative approach allowed the glue to fill the aneurysmal volume without significant risk of migration to non-target vessels. The precise formulation provided enough working time for the controlled and accurate filling of the aneurysm, avoiding premature adhesion to the microcatheter.
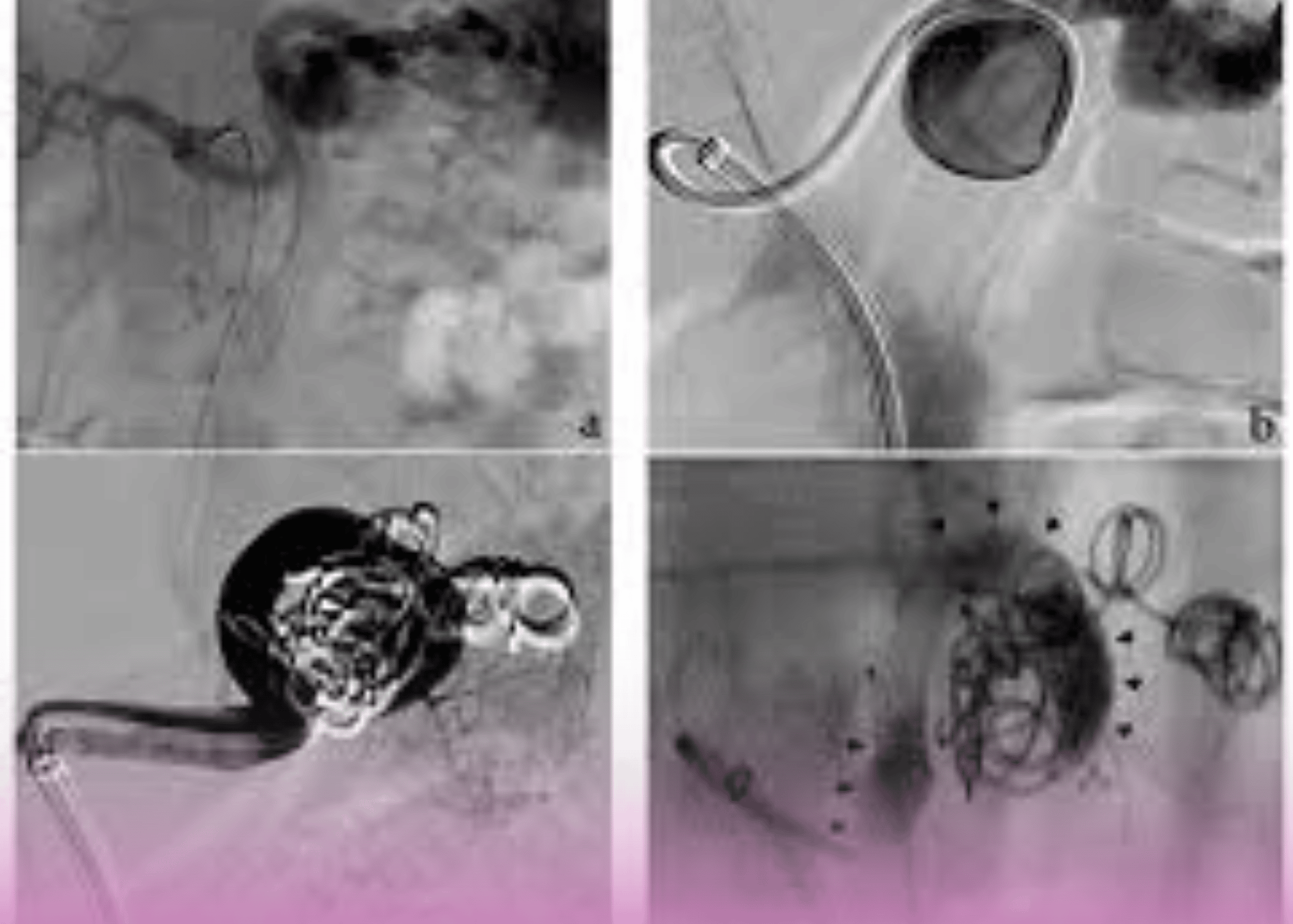
Procedural Images
The interventional series clearly demonstrates the progression of this novel technique:
- Initial angiogram showing the left hepatic artery aneurysm
- Post-coiling control angiogram with the established coil framework
- Final angiogram after glue injection showing the dense embolization material contained within the coil cage and complete exclusion of the aneurysm from circulation
Clinical Significance
This case demonstrates several important innovations in interventional radiology:
- Adaptable Technical Solutions: By combining existing tools (coils and glue) in a novel approach, complex vascular abnormalities can be treated without requiring specialized devices that may not be immediately available.
- Tailored Treatment Approach: The coil-cage technique provided structural integrity while the liquid embolic agent ensured complete filling of the irregular aneurysm, addressing the unique challenges of this specific case.
- Minimally Invasive Management: The endovascular approach avoided the need for open surgery in a patient with multiple vascular abnormalities, potentially reducing recovery time and complications.
- Comprehensive Vascular Assessment: The identification of bilateral renal artery dissections highlights the importance of complete vascular evaluation in patients with any arterial abnormality.
Conclusion
The successful treatment of this complex hepatic artery aneurysm through an innovative combined coil-and-glue technique showcases Burjeel Hospital Abu Dhabi’s commitment to advancing interventional radiology solutions for life-threatening conditions. Dr. Almarzooqi’s approach demonstrates how technical creativity and expertise can produce excellent outcomes in challenging cases, furthering the field of minimally invasive vascular interventions.