Patient Presentation
A 66-year-old male presented with symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) that had become increasingly refractory to medical management. His symptoms included weak urinary stream, increased frequency of micturition, sensation of incomplete bladder emptying, nocturia (4-5 times nightly), and urgency.
Diagnostic Findings
Ultrasound examination revealed a significantly enlarged prostate measuring approximately 180 grams with post-void residual urine exceeding 200 ml.
Treatment Considerations
Our Consultant Urologist, Dr. Qaraschouli thoroughly discussed all available surgical options with the patient and his family, including:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
- Holmium laser enucleation
- Other laser therapy options
- Steam therapy (Resume)
- Open transvesical prostatectomy
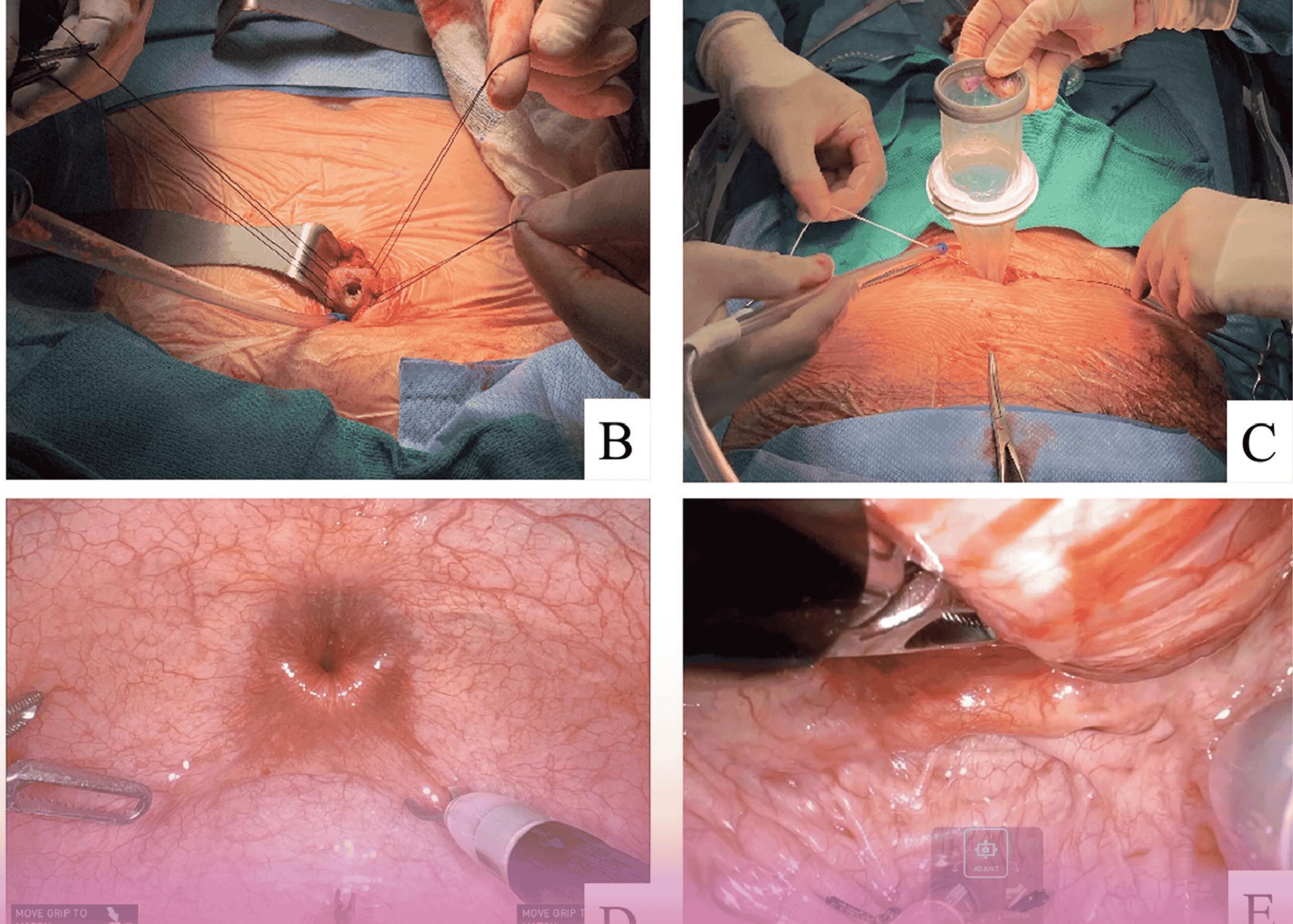
After careful consideration of the massive prostate size and the patient’s clinical presentation, the decision was made to proceed with open transvesical prostatectomy.
Surgical Outcome
The surgical and postoperative courses were uneventful. Following removal of the indwelling catheter, the patient experienced satisfactory micturition with only mild stress incontinence (Grade 1) during the first postoperative week, which subsequently resolved completely. Follow-up ultrasound confirmed the absence of residual urine, in stark contrast to the preoperative findings.
Histopathology confirmed prostatic adenoma with chronic prostatitis, with no evidence of malignancy.
The Continued Relevance of Open Surgery
These cases demonstrate that open surgery remains the optimal choice in specific urological scenarios. Key advantages in these cases included:
- For Complex Renal Tumors:
- Better control of bleeding in high-risk patients with coagulopathy
- Reduced operative time in patients with multiple comorbidities
- Enhanced ability to manage unexpected intraoperative findings
- Lower risk of major vascular complications
- For Massive Prostatic Hyperplasia:
- Complete removal of prostatic adenoma regardless of size
- Definitive solution with lower recurrence rates compared to some minimally invasive approaches
- Shorter operative duration in cases of extremely enlarged prostates
- Excellent functional outcomes with rapid recovery
Conclusion
While minimally invasive and robotic approaches continue to advance, these cases from Burjeel Royal Hospital Asharej highlight that open surgical techniques remain essential tools in the modern urologist’s armamentarium. The surgical team’s ability to select the most appropriate surgical approach based on individual patient factors—rather than simply following technological trends—represents the true art of surgical practice. This patient-centered approach ensures optimal outcomes in complex urological cases where traditional open techniques may still offer significant advantages.