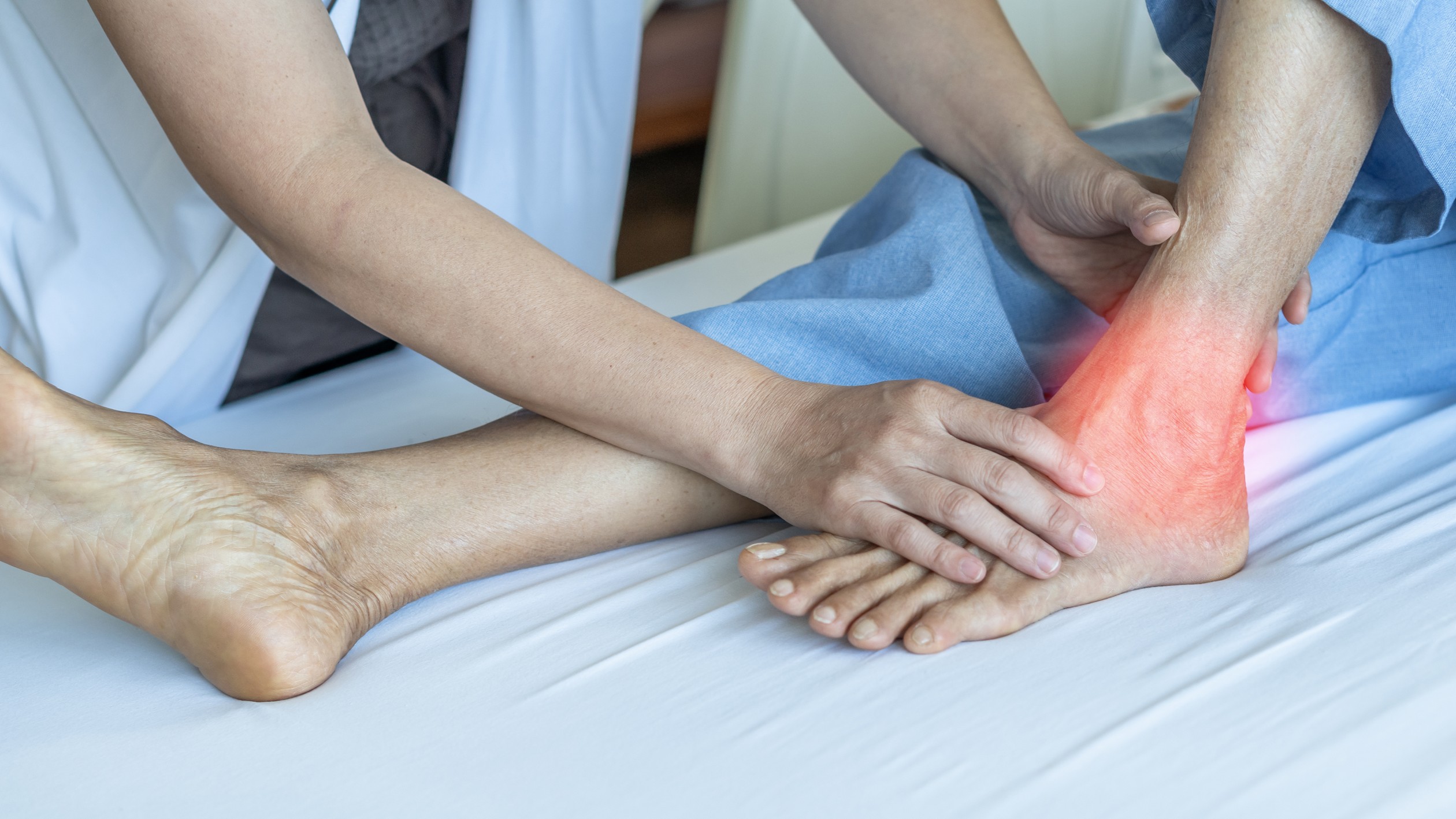
Chronic ankle instability is persistent pain on the outside of your ankles, usually occurs after you suffer from an ankle sprain that is not healed completely. The pain typically will appear whenever you engage in some kind of physical activity & often lead you to feel instability on your ankle area while applying weight.
What are the parts of the ankle?
Ankle joint is made of up of two bones of lower leg namely “tibia” & “fibula” and first bone of your foot is called as talus. These bony structures are stabilized by ligaments and tendons. Your outer part of the ankle is supported by Lateral collateral ligament, your inner part of the ankle is supported by Medial collateral ligament.
What is ankle sprain?
The tissues which connect bone to bone are called as ligament. When you sprain your ankle, one or more of your ligaments are stretched or torn, causing damage to the ligaments & tendons around the ankle. Tendon is the part of the muscle which is directly connected to the bone. 20% of the people who had an ankle injury may develop chronic ankle instability if it’s not taken care of.
How does the ankle instability feel like?
- Pain on the outside of your ankle
- Tenderness around the ankle
- The feeling your ankle is going to “give out.”
- Stiffness
- Chronic discomfort and swelling
How is chronic instability is diagnosed?
To determine whether you have a chronic ankle instability the orthopedic doctor especially foot and ankle doctor, will ask your duration of the symptoms, and we will conduct detained physical examination which includes some kind of special tests and functional tests, if required he may order for imaging (X-ray/Ultrasound/MRI) studies for your ankle. Based on the collective information chronic instability is diagnosed.
How is the chronic ankle instability treated?
Most of the time chronic ankle instability is treated without surgery. In severe cases of ankle instability doctor may recommend for surgery which is minimally invasive procedure, which is often done as a day care surgery (on the same day of surgery you can go home).
When should you consider Surgery?
- When the ligament is stretched beyond the point of physiological limit.
- Complete rupture of the ligament.
- Presence of loose body within the joint.
- Excessive amount of damage to joint surface (Articular cartilage)
What is the conservative management for chronic ankle instability?
- Anti-inflammatory medicine
- Physical therapy
- Bracing.
What is the role of Physiotherapy in chronic ankle instability?
Physical therapist will assess other joints of your involved leg like hip and knee to identify if there are any contributing factors from these uninvolved joints caused your initial ankle sprain. Studies suggest that weakness of the hip muscles is one of the leading causes for ankle injuries in professional athletes and in common population as well.
After the detailed assessment your Physiotherapist will decide your plan of care based on your activity levels, and goal to be attained in general therapy plan can be divided as pain management and graded exercise program.
What is the pain management delivered by the physiotherapist?
- Soft tissue massage.
- Joint mobilization.
- Laser therapy.
- TECAR therapy.
Usually pain management treatments are based on the structures (Ligaments/Tendon/Articular surface) involved.
What kind of exercises you will do?
Exercise program is based on extend of your injury, your activity level before the injury and what are your goals – like getting back to any kind of sports are activity. Usually, it’s ranging from basic range of motion exercises, flexibility exercises, strengthening exercises and proprioception exercises (exercises to regain the joint control).
The most important thing to remember is the torn ligaments in your ankle need to heal, so you need to rest from any activity that might be aggravating your pain.