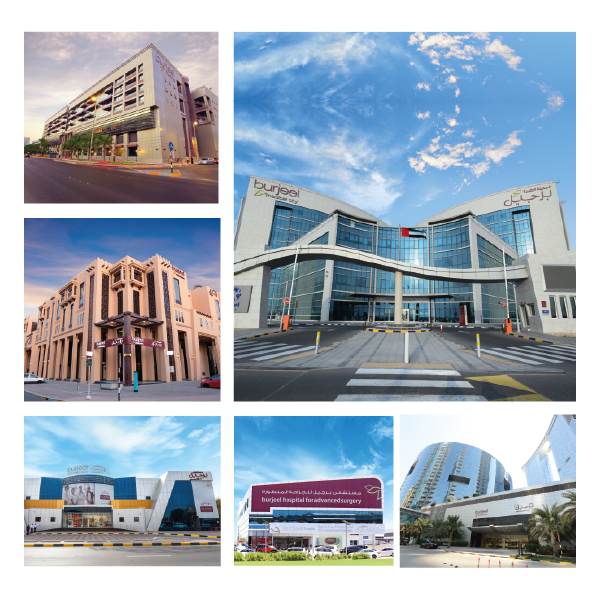
Burjeel Holdings's premium healthcare brand, Burjeel is the most comprehensive private tertiary healthcare provider in UAE. The Burjeel hospitals have been at the forefront of healthcare services in the region and have emerged as the Center of Medical Excellence across the UAE. Over the years, Burjeel has built a strong sense of trust in the hearts of every patient we came across by serving them in all walks of life along with state-of-the-art facilities, and in-depth expertise.
While we embrace advanced technologies, we also believe in providing compassionate care in amalgam with medical care to every patient. Our world-renowned doctors and the dedicated team behind Burjeel work every day to provide the patients with a seamless healthcare experience to be cherished in their heart.
Why Choose Us?

Our Values

Balance
We create a guaranteed work-life balance for everyone working under Burjeel.
Unity
We believe success can only be achieved with shared goals, mutual trust, and effective communication of a wonderful team.
Respect
We treat everyone with dignity and value every contribution, view, and interest.

Justice
We ensure that premium healthcare services are provided to all.

Efficiency
We make careful use of resources to obtain the best possible outcomes.

Empowerment
We encourage our employees to bring out their individual talent and capabilities which in turn helps to further the shared mission of Burjeel Hospital.

Leadership
We lead innovations to make healthcare accessible to everyone, everywhere.
Vision
Burjeel Hospital looks forward to being the most trusted and respected healthcare service provider in the Middle East by treating every human life placed in our hands with utmost care and raising the standards of healthcare.
Mission
Burjeel Hospital will deliver exemplary medical care by combining state-of-the-art technology and highly skilled medical experts to provide care with the human touch.
Leadership Team
We as healthcare leaders believe in making a positive difference in the lives of our patients and employees.

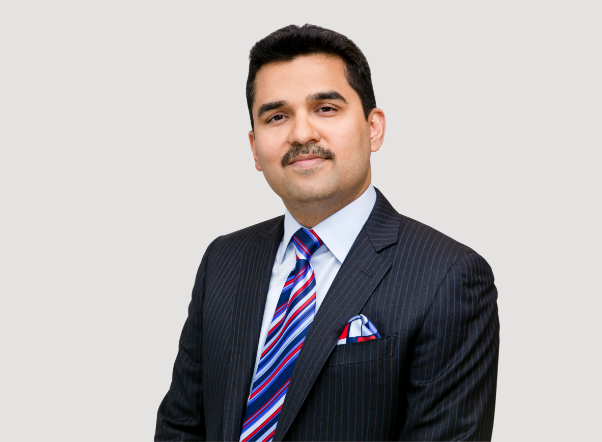
Mr. John Sunil
Group Chief Executive Officer, Burjeel Holdings



