-
Anesthesiology
-
Cardiology
-
Dietetics and Nutrition
-
Emergency Clinic
-
Foot and Ankle Clinic
-
General and Laparoscopic Surgery
-
Gynecology and Obstetrics
-
Hand Surgery
-
Hematology
-
Hip Surgery
-
Internal Medicine
-
Joint Replacement
-
Knee Surgery
-
Laboratory
-
Neurology
-
Neurosurgery
-
Oncology
-
Orthopedics and Sports Medicine
-
Pain Management
-
Pediatric Orthopedics
-
Physiotherapy
-
Plastic, Aesthetic and Reconstructive Surgery
-
Scoliosis Surgery
-
Shoulder Surgery
-
Spine Surgery
-
Sports Orthopedics
-
Urology
-
Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
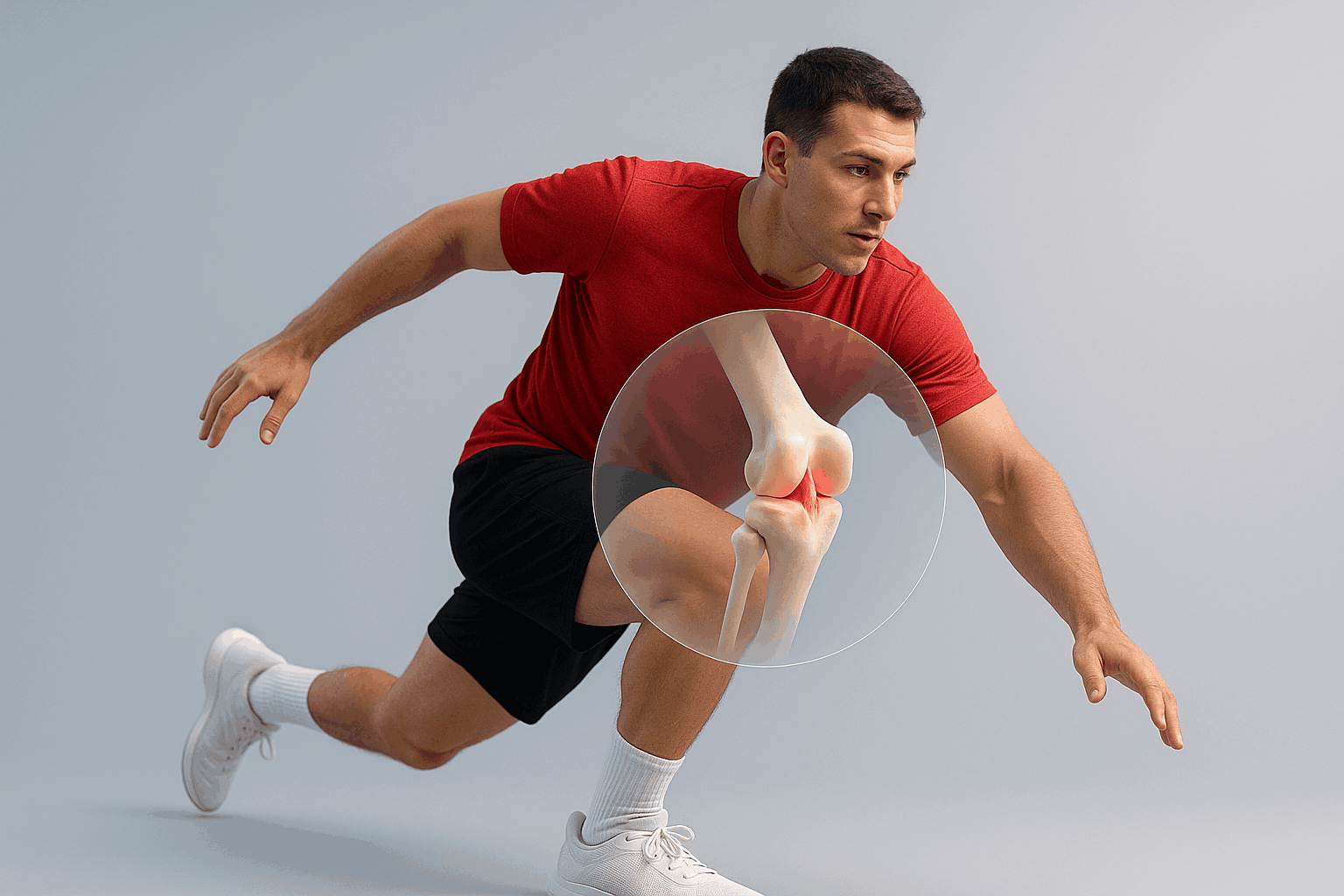
What is a Hip Replacement?
A hip replacement is a surgical procedure where an orthopedic surgeon replaces your damaged hip joint with an artificial implant (prosthesis). This surgery is often recommended for people with severe hip pain and stiffness that interferes with daily activities, despite trying nonsurgical treatments like medication and physical therapy.
Types of Hip Replacements
There are two main types of hip replacements:
- Total Hip Replacement: This is the most common type, where the surgeon replaces the entire hip joint, including the ball (femoral head) of your thighbone and the socket (acetabulum) it fits into.
- Partial Hip Replacement: This is less common and only replaces a part of the hip joint, typically used for specific fractures or tumors.
Who Needs a Hip Replacement?
Hip replacements are most often considered for patients whose hip pain significantly impacts their daily life. Arthritis is the leading cause of hip pain, with the most common types affecting the hip being:
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
Other conditions that can damage the hip joint and require replacement include:
- Osteonecrosis (bone death)
- Severe fractures
- Hip impingement
- Hip dysplasia (abnormal development of the hip joint)
- Tumors
How Common are Hip Replacements?
Hip replacement is a common surgery, with over 350,000 procedures performed annually in the US alone.
Before Your Hip Replacement
Your surgeon will conduct a physical exam and order tests like X-rays, blood tests, and potentially additional imaging (MRI, CT scan) to assess your hip joint and overall health before surgery. They will also discuss your medical history, medications, and expectations for the procedure.
The Hip Replacement Procedure
Hip replacements are typically performed under regional anesthesia, which numbs the area around the hip but keeps you awake. The surgeon removes the damaged parts of your hip joint and replaces them with the prosthetic implant, usually made of metal, plastic, or ceramic. The surgery typically takes 1-2 hours.
After Your Hip Replacement
Most hip replacements are outpatient procedures, meaning you can go home the same day or stay overnight for observation. Recovery involves physical therapy to regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in your hip. It usually takes several months for full recovery.
Benefits of Hip Replacement
Hip replacements are highly successful in significantly reducing pain and stiffness, allowing for improved mobility and range of motion. This can lead to a better quality of life with increased ability to walk, climb stairs, and participate in daily activities.
Risks and Complications
Complications from hip replacements are uncommon but can include:
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Issues with the implant (loosening, dislocation)
- Bone fractures
- Stiffness
Recovery and Outlook
Recovery from hip replacement surgery varies, but typically takes several months. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in regaining strength and movement. Most people regain full use of their hip within 6-12 months. Modern prosthetics typically last a lifetime, but some patients may require future surgery.
When to Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor immediately after hip replacement if you experience:
- Severe pain
- Bleeding or drainage from the incision site
- Swelling
- Redness or discoloration around the incision
Hip Replacement for Patients Over 70
While age doesn’t guarantee a specific recovery timeline, people over 70 may take longer to recover from hip replacement surgery. The most important factor is focusing on progress and improvement in movement and hip function throughout physical therapy.
Does Hip Replacement Cure Arthritis?
No, hip replacement doesn’t cure arthritis. It removes the damaged joint and relieves symptoms like pain and stiffness, but doesn’t address the underlying condition itself.
Burjeel Hospital Dubai: Your Partner in Hip Replacement Care
At Burjeel Hospital Dubai, our experienced orthopedic surgeons offer advanced hip replacement surgery to help you regain mobility and improve your quality of life. We provide comprehensive care, from pre-surgical evaluation to post-operative rehabilitation, to ensure a successful outcome.
Hip Arthroscopy
Revision Hip Surgery
Surgical Dislocation
Minimally Invasive Total Hip Replacement
Total Hip Resurfacing
Dedicated Hip Therapy
Fluoroscopic Guided Hip Injection
Book Appointment with our Experts
Blogs

Vitamin D Deficiency Treatment: Comprehensive Guide to Boosting Your Levels Naturally
Read more
Understanding Vitamin D Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
Read more
Shoulder Pain Management: Your Comprehensive Guide
Read more