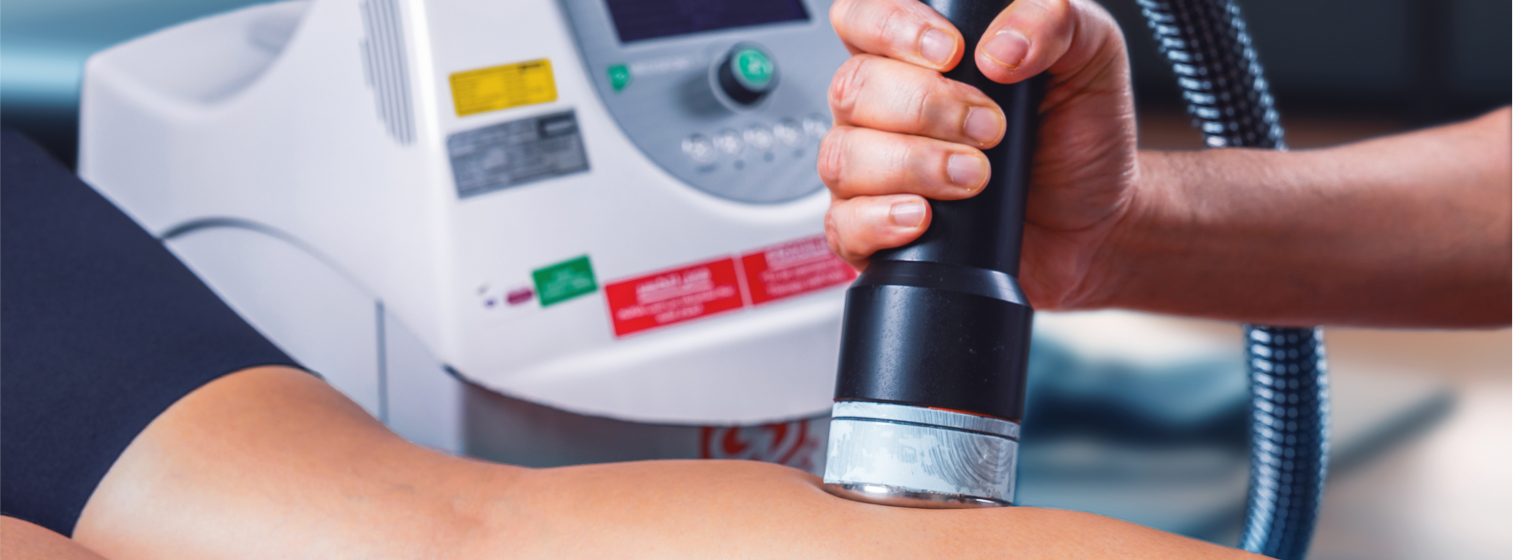
Significances
Tissue Healing
Ultrasound therapy promotes tissue healing by increasing blood flow, stimulating collagen production, and enhancing cellular metabolism, accelerating the repair of damaged tissues.
Pain Reduction
By stimulating nerve fibers and blocking pain signals, ultrasound therapy alleviates pain and discomfort associated with various musculoskeletal conditions, injuries, and inflammatory conditions.
Muscle Relaxation
Ultrasound therapy provides deep heat to muscles, tendons, and ligaments, promoting muscle relaxation, reducing muscle spasms, and enhancing flexibility and range of motion.
Edema Reduction
Ultrasound therapy facilitates the absorption of excess fluid and swelling from injured tissues, reducing edema and promoting lymphatic drainage, leading to improved tissue healing and recovery.
Scar Tissue Management
Ultrasound therapy helps break down scar tissue and adhesions, promoting tissue remodeling and flexibility, particularly in post-surgical or traumatic injuries.
Measures to Support
Comprehensive Assessment
Undergo a thorough evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional, such as a physical therapist or rehabilitation specialist, to assess the nature and severity of the injury or condition and determine the appropriateness of ultrasound therapy as a treatment modality.
Individualized Treatment Plan
Work with your healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan incorporating ultrasound therapy sessions, frequency, and duration tailored to your specific needs, goals, and condition.
Proper Application
Ensure proper application of ultrasound therapy by a trained healthcare provider, following established protocols and guidelines for ultrasound parameters, including frequency, intensity, and duration of treatment.
Skin Protection
Use appropriate coupling agents, such as ultrasound gel, to facilitate the transmission of sound waves and protect the skin during ultrasound therapy sessions, minimizing the risk of skin irritation or burns.
Communication and Feedback
Communicate any discomfort, changes in symptoms, or adverse reactions experienced during or after ultrasound therapy sessions with your healthcare provider, to ensure safe and effective treatment delivery and optimize outcomes.
Compliance and Follow-Up
Adhere to prescribed ultrasound therapy protocols, attend scheduled treatment sessions, and communicate regularly with your healthcare provider to monitor progress, address concerns, and adjust treatment as needed to optimize outcomes.